Cognitive Distortions Guide: Understand Your Thoughts
Cognitive distortions are irrational or exaggerated thought patterns that can negatively impact an individual's mental health and well-being. These distortions can lead to inaccurate perceptions, poor decision-making, and unhealthy behaviors. Understanding cognitive distortions is essential for developing effective coping strategies and improving mental health outcomes. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the world of cognitive distortions, exploring their types, causes, and consequences, as well as providing expert insights and practical advice for overcoming these distortions.
Introduction to Cognitive Distortions

Cognitive distortions were first introduced by psychologist Aaron Beck in the 1960s. Beck proposed that negative thought patterns, such as all-or-nothing thinking and catastrophizing, contribute to the development and maintenance of mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. Since then, researchers have identified numerous cognitive distortions, each with its unique characteristics and effects on mental health. Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT) is a widely used therapeutic approach that aims to identify and challenge these distortions, promoting more balanced and constructive thinking patterns.
Types of Cognitive Distortions
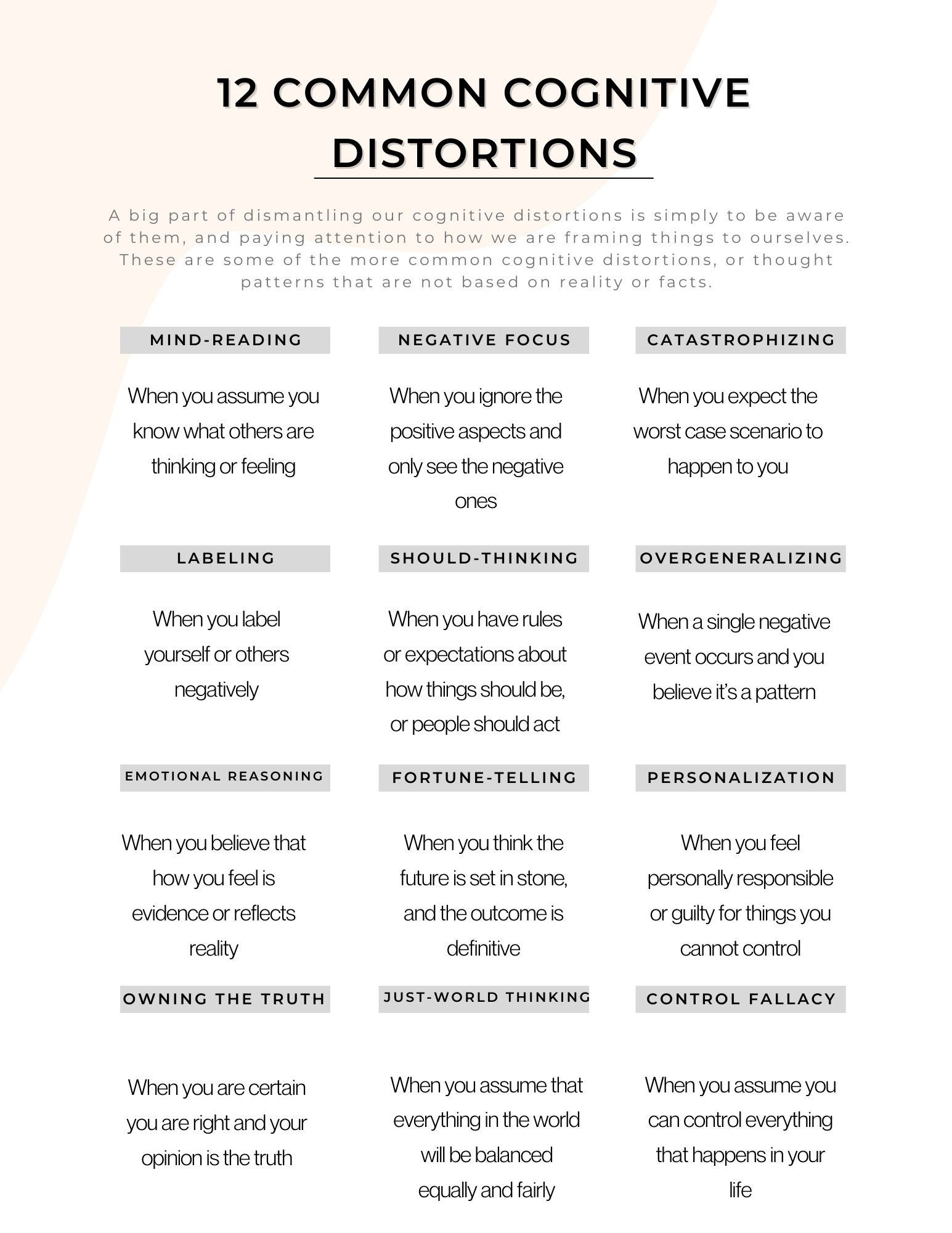
There are several types of cognitive distortions, including:
- All-or-nothing thinking: viewing situations as either entirely good or entirely bad
- Overgeneralization: making sweeping conclusions based on limited evidence
- Mental filtering: focusing on negative aspects while ignoring positive ones
- Disqualifying the positive: downplaying or dismissing positive experiences or achievements
- Jumping to conclusions: making assumptions without sufficient evidence
- Magnification: exaggerating the importance or severity of a situation
- Minimization: downplaying the significance or impact of a situation
- Emotional reasoning: assuming that emotions reflect reality
- Should statements: using absolute language, such as “should,” “must,” or “ought to”
- Labeling: assigning a negative label to oneself or others
- Personalization: taking things personally or blaming oneself for events outside of one’s control
Causes and Consequences of Cognitive Distortions

Cognitive distortions can arise from various factors, including genetic predisposition, environmental influences, and past experiences. For example, individuals with a family history of mental health disorders may be more prone to developing cognitive distortions. Additionally, traumatic events, social learning, and cultural norms can contribute to the development of these distortions. The consequences of cognitive distortions can be severe, leading to:
- Anxiety and depression
- Low self-esteem and self-confidence
- Strained relationships and social isolation
- Impaired decision-making and problem-solving
- Reduced resilience and stress management
Overcoming Cognitive Distortions
Fortunately, cognitive distortions can be addressed and overcome through a combination of self-awareness, education, and therapeutic interventions. Some effective strategies for overcoming cognitive distortions include:
- Cognitive restructuring: identifying and challenging distorted thoughts
- Mindfulness and meditation: practicing present-moment awareness and acceptance
- Journaling and self-reflection: monitoring thoughts and emotions to identify patterns and areas for improvement
- Social support and therapy: seeking help from mental health professionals and supportive networks
| Cognitive Distortion | Example | Challenge |
|---|---|---|
| All-or-nothing thinking | "I'm a complete failure because I made one mistake." | "I made a mistake, but that doesn't define my entire worth or abilities." |
| Overgeneralization | "I'll never be able to do this because I failed once before." | "I learned from my past experience, and I can try again with a new approach." |
| Mental filtering | "This event was a total disaster because of one negative aspect." | "There were both positive and negative aspects to the event; I'll focus on the positive and learn from the negative." |

Future Implications and Research Directions

As research on cognitive distortions continues to evolve, it is essential to explore new avenues for prevention, diagnosis, and treatment. Some potential areas of focus include:
- Neuroimaging studies: investigating the neural mechanisms underlying cognitive distortions
- Personalized interventions: developing tailored therapeutic approaches based on individual profiles and needs
- Technology-based interventions: leveraging digital platforms and tools to promote cognitive restructuring and mental health support
- Cultural and sociological factors: examining the impact of cultural norms, social media, and environmental influences on cognitive distortions
What is the most common cognitive distortion?
+One of the most common cognitive distortions is all-or-nothing thinking, which involves viewing situations as either entirely good or entirely bad. This distortion can lead to oversimplification and neglect of nuances, resulting in poor decision-making and relationships.
How can I identify cognitive distortions in my thoughts?
+To identify cognitive distortions, start by monitoring your thoughts and emotions, particularly in situations that trigger strong reactions. Look for patterns, such as absolute language, overgeneralization, or mental filtering. Keeping a thought journal or seeking feedback from trusted friends or therapists can also help you become more aware of your thought patterns and identify potential distortions.
Can cognitive distortions be overcome without therapy?
+While therapy can be an effective way to address cognitive distortions, it is possible to overcome them without professional help. This can be achieved through self-awareness, education, and practice. By learning to recognize and challenge distorted thoughts, individuals can develop more balanced and constructive thinking patterns. However, for more severe or persistent distortions, seeking guidance from a mental health professional may be necessary.



