Brain Cancer Ct Scan

Brain cancer is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition that affects thousands of people worldwide. One of the most effective ways to diagnose and monitor brain cancer is through the use of computed tomography (CT) scans. A CT scan is a non-invasive medical imaging test that uses X-rays and computer technology to produce detailed cross-sectional images of the brain and other parts of the body. In the context of brain cancer, CT scans play a crucial role in detecting tumors, evaluating the extent of disease, and monitoring treatment response.
Overview of Brain Cancer CT Scans
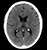
A brain cancer CT scan typically involves the use of a contrast agent, which is a special dye that is injected into the bloodstream to highlight the tumor and surrounding tissues. The scan itself is usually performed in a hospital or imaging center, and the entire process typically takes around 30 minutes to an hour to complete. During the scan, the patient lies on a table that slides into a large, doughnut-shaped machine, which uses X-rays to capture images of the brain from different angles. The resulting images are then reconstructed into detailed, three-dimensional pictures of the brain, which can be used to diagnose and monitor brain cancer.
Types of Brain Cancer CT Scans
There are several types of CT scans that can be used to diagnose and monitor brain cancer, including:
- Non-contrast CT scan: This type of scan does not use a contrast agent and is often used to detect acute bleeding or other emergencies.
- Contrast-enhanced CT scan: This type of scan uses a contrast agent to highlight the tumor and surrounding tissues, and is often used to evaluate the extent of disease and monitor treatment response.
- CT angiography: This type of scan uses a contrast agent to visualize the blood vessels in the brain and is often used to diagnose and treat vascular malformations or other conditions.
- CT perfusion scan: This type of scan uses a contrast agent to evaluate blood flow to the brain and is often used to diagnose and monitor conditions such as stroke or brain cancer.
| Type of CT Scan | Description | Indications |
|---|---|---|
| Non-contrast CT scan | Does not use contrast agent | Acute bleeding, emergencies |
| Contrast-enhanced CT scan | Uses contrast agent to highlight tumor | Evaluating extent of disease, monitoring treatment response |
| CT angiography | Visualizes blood vessels in brain | Diagnosing and treating vascular malformations |
| CT perfusion scan | Evaluates blood flow to brain | Diagnosing and monitoring stroke or brain cancer |
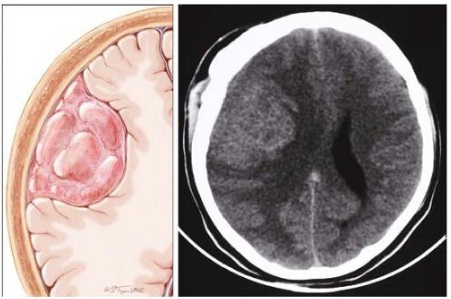
Interpreting Brain Cancer CT Scan Results
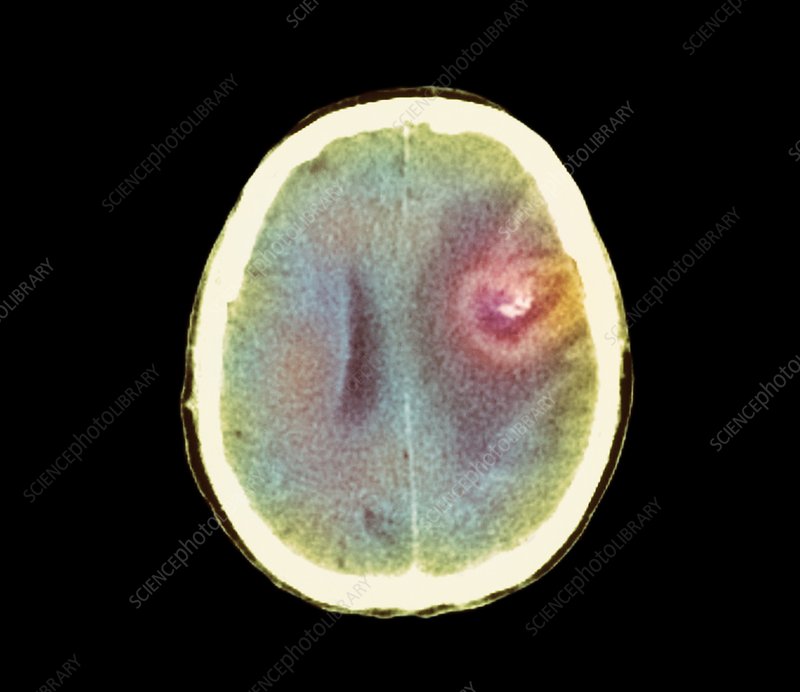
Interpreting the results of a brain cancer CT scan requires specialized training and expertise. Radiologists and other healthcare professionals use a combination of visual inspection and computer-aided detection to identify abnormalities and diagnose brain cancer. The results of the scan are typically reported in terms of the size, location, and characteristics of the tumor, as well as any evidence of disease spread or other complications.
Limitations and Potential Risks of Brain Cancer CT Scans
While CT scans are a powerful tool for diagnosing and monitoring brain cancer, they are not without limitations and potential risks. Some of the limitations and risks associated with brain cancer CT scans include:
- Radiation exposure: CT scans use X-rays, which can expose patients to ionizing radiation and increase the risk of cancer and other health problems.
- Contrast agent reactions: Some patients may be allergic to the contrast agent used in CT scans, which can cause a range of symptoms from mild discomfort to life-threatening reactions.
- Image quality: The quality of the images produced by a CT scan can be affected by a range of factors, including patient movement, metal artifacts, and technical limitations of the scanner.
In order to minimize the risks and limitations associated with brain cancer CT scans, it is essential to carefully select patients for scanning, use the lowest possible dose of radiation and contrast agent, and ensure that scans are performed and interpreted by qualified healthcare professionals.
What is the purpose of a brain cancer CT scan?
+A brain cancer CT scan is used to diagnose and monitor brain cancer, including detecting tumors, evaluating the extent of disease, and monitoring treatment response.
What are the different types of brain cancer CT scans?
+There are several types of brain cancer CT scans, including non-contrast CT scans, contrast-enhanced CT scans, CT angiography, and CT perfusion scans. Each type of scan has its own specific indications and uses.
What are the limitations and potential risks of brain cancer CT scans?
+The limitations and potential risks of brain cancer CT scans include radiation exposure, contrast agent reactions, and image quality limitations. To minimize these risks, it is essential to carefully select patients for scanning, use the lowest possible dose of radiation and contrast agent, and ensure that scans are performed and interpreted by qualified healthcare professionals.



