Bv In Men: Symptoms & Treatment
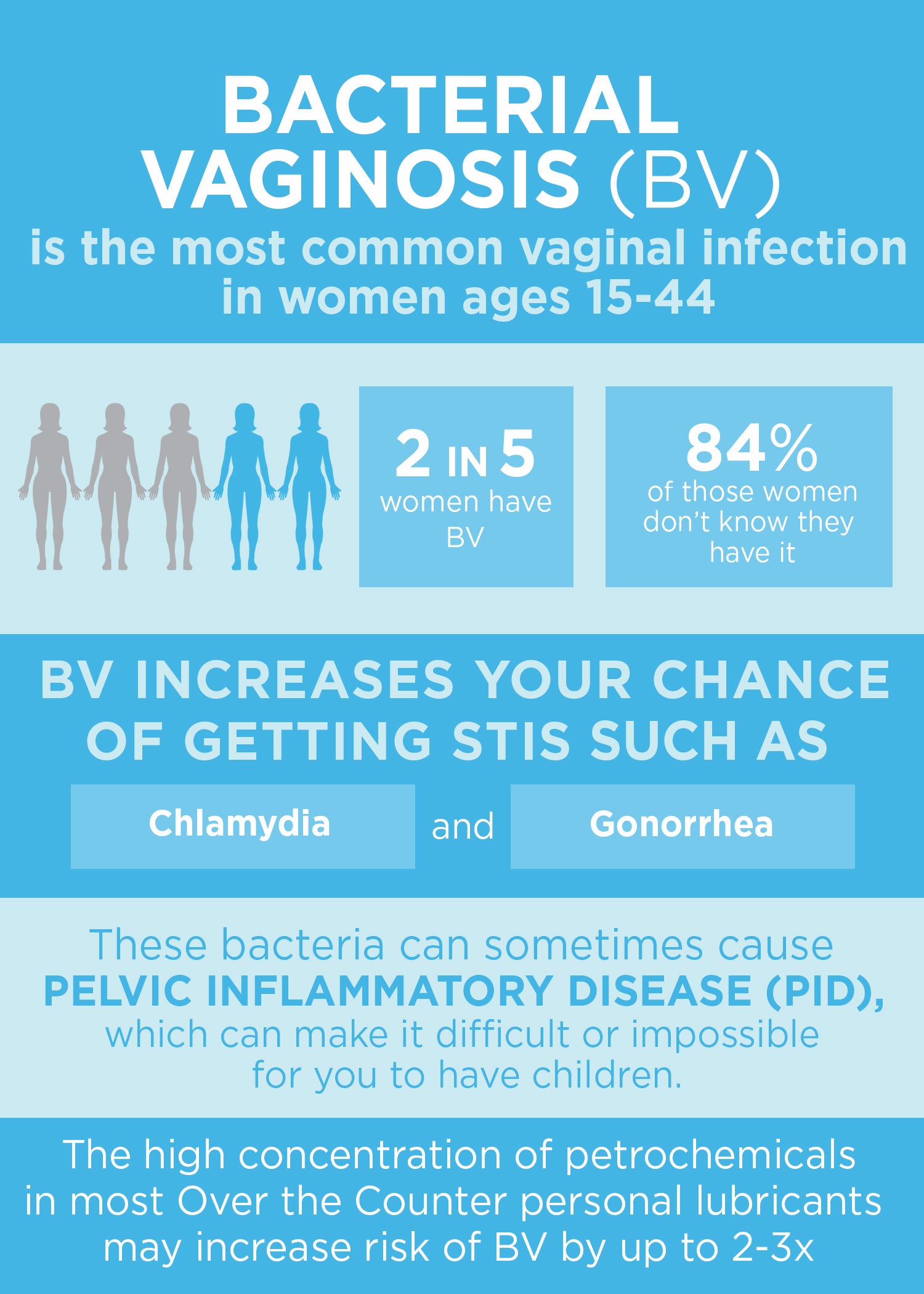
Bacterial vaginosis (BV) is a common vaginal infection in women, but it can also affect men, albeit in different ways. While men cannot contract BV in the same manner as women, they can be carriers of the bacteria that cause the infection. In this article, we will explore the symptoms and treatment options for BV in men, as well as the implications for their health and relationships.
Understanding Bacterial Vaginosis in Men

BV is caused by an imbalance of naturally occurring bacteria in the vagina. In women, this imbalance can lead to symptoms such as abnormal vaginal discharge, odor, and irritation. Men, on the other hand, can carry the bacteria that cause BV without exhibiting any symptoms. However, if a man has unprotected sex with a partner who has BV, he can become a carrier of the bacteria and potentially transmit it to other partners.
Symptoms of BV in Men
While men do not typically exhibit symptoms of BV, they may experience some signs if they have contracted the bacteria. These can include:
- Urethritis: inflammation of the urethra, which can cause symptoms such as burning during urination, discharge, and irritation
- Epididymitis: inflammation of the epididymis, a tube at the back of the testicle that stores and carries sperm, which can cause symptoms such as pain, swelling, and discharge
- Prostatitis: inflammation of the prostate gland, which can cause symptoms such as pain, discomfort, and urinary problems
It is essential to note that these symptoms can also be caused by other conditions, so it is crucial to consult a healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment.
Treatment Options for BV in Men

Treatment for BV in men typically involves antibiotics, which can help eliminate the bacteria that cause the infection. The most commonly prescribed antibiotics for BV in men are:
| Antibiotic | Dosage |
|---|---|
| Metronidazole | 500mg twice daily for 7-10 days |
| Clindamycin | 300mg twice daily for 7-10 days |

It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by the healthcare provider, even if symptoms improve before finishing the treatment. This will help ensure that the infection is fully cleared and reduce the risk of transmission to partners.
Prevention and Transmission
To prevent the transmission of BV, it is crucial to practice safe sex, including using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners. Men who have been diagnosed with BV or have a partner with BV should also take steps to reduce their risk of transmission, such as:
- Using condoms consistently and correctly during vaginal, anal, and oral sex
- Avoiding sharing sex toys or using them without proper cleaning and disinfection
- Getting tested regularly for STIs, including BV
Implications for Relationships and Sexual Health

BV can have significant implications for relationships and sexual health, particularly if left untreated. Men who have BV or have a partner with BV may experience:
- Stigma and shame: BV can be stigmatized, leading to feelings of shame and guilt
- Relationship problems: BV can cause tension and conflict in relationships, particularly if one partner is not willing to seek treatment
- Sexual dysfunction: BV can cause symptoms such as pain and discharge, which can make sex uncomfortable or painful
It is essential for men to prioritize their sexual health and seek treatment if they suspect they have BV or have a partner with BV. By seeking treatment and practicing safe sex, men can reduce their risk of transmission and help protect their relationships and overall health.
Can men transmit BV to their partners?
+Yes, men can transmit BV to their partners through unprotected sex. If a man has BV, he can carry the bacteria that cause the infection and potentially transmit it to his partners.
How can men prevent BV?
+Men can prevent BV by practicing safe sex, including using condoms and limiting the number of sexual partners. They should also get tested regularly for STIs, including BV, and seek treatment if they suspect they have the infection.
Can BV be cured?
+Yes, BV can be cured with antibiotics. However, it is essential to complete the full course of treatment as prescribed by the healthcare provider to ensure that the infection is fully cleared.
In conclusion, BV is a significant public health concern that affects not only women but also men. By understanding the symptoms, treatment options, and implications for relationships and sexual health, men can take steps to protect themselves and their partners from the infection. It is essential for men to prioritize their sexual health and seek treatment if they suspect they have BV or have a partner with BV.