12 Liquid Tips For Easy Evaporation
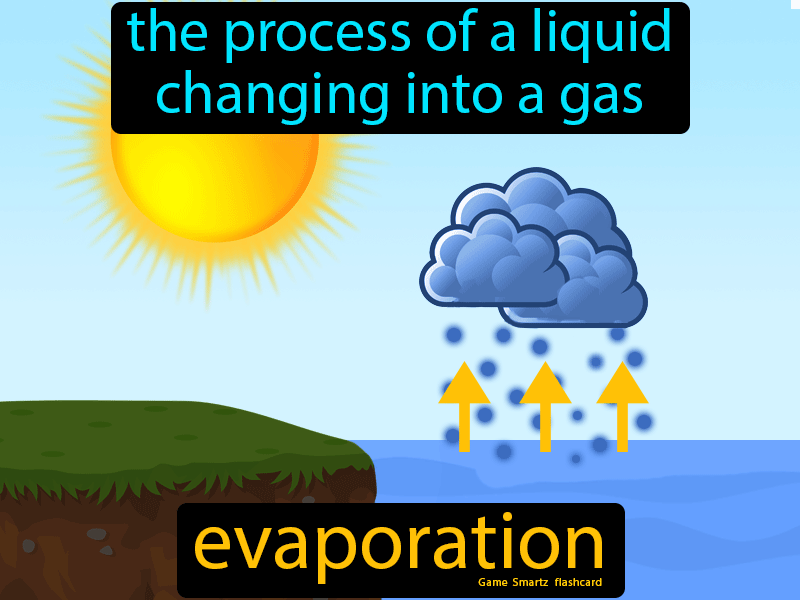
Evaporation is a fundamental process in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. It involves the transformation of a liquid into a gas or vapor. Understanding the factors that influence evaporation is crucial for optimizing processes and achieving desired outcomes. In this context, we will explore 12 liquid tips for easy evaporation, providing a comprehensive overview of the principles and practices involved.
Understanding Evaporation Fundamentals

Evaporation occurs when a liquid is heated, and the molecules gain sufficient energy to break free from the surface tension and turn into vapor. The rate of evaporation depends on several factors, including temperature, humidity, and air flow. By manipulating these conditions, it is possible to enhance or reduce the evaporation rate. For instance, increasing the temperature or reducing the humidity can accelerate evaporation, while decreasing the temperature or increasing the humidity can slow it down.
Factors Influencing Evaporation Rate
The evaporation rate is also affected by the surface area of the liquid, the intermolecular forces between the molecules, and the presence of impurities. A larger surface area can increase the evaporation rate, as more molecules are exposed to the air. Strong intermolecular forces, such as hydrogen bonds, can slow down evaporation, while weak forces can facilitate it. Impurities can either enhance or inhibit evaporation, depending on their nature and concentration.
| Factor | Effect on Evaporation Rate |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Increases with temperature |
| Humidity | Decreases with humidity |
| Air Flow | Increases with air flow |
| Surface Area | Increases with surface area |
| Intermolecular Forces | Decreases with strong forces |
| Impurities | Varies depending on impurity |

12 Liquid Tips for Easy Evaporation
Based on the fundamental principles of evaporation, the following 12 liquid tips can facilitate easy evaporation:
- Use a shallow container: A shallow container can increase the surface area of the liquid, allowing more molecules to evaporate.
- Apply heat: Heating the liquid can provide the necessary energy for the molecules to break free and evaporate.
- Reduce humidity: Low humidity can enhance evaporation by reducing the amount of moisture in the air.
- Increase air flow: Air flow can facilitate evaporation by removing the vapor and allowing more molecules to escape.
- Use a fan: A fan can increase air flow and enhance evaporation.
- Reduce intermolecular forces: Weak intermolecular forces can facilitate evaporation by allowing molecules to break free more easily.
- Remove impurities: Impurities can affect evaporation, and removing them can help achieve the desired outcome.
- Use a desiccant: A desiccant can absorb moisture and reduce humidity, enhancing evaporation.
- Increase the surface area: Increasing the surface area of the liquid can allow more molecules to evaporate.
- Use a spray or mist: A spray or mist can increase the surface area of the liquid and facilitate evaporation.
- Apply vacuum: Applying a vacuum can reduce the pressure and enhance evaporation.
- Monitor temperature: Monitoring the temperature can help optimize the evaporation process and achieve the desired outcome.
Applications of Easy Evaporation
Easy evaporation has numerous applications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. Some examples include:
- Distillation: Evaporation is used to separate mixtures based on their boiling points.
- Crystallization: Evaporation is used to form crystals from a solution.
- Drying: Evaporation is used to remove moisture from materials.
- Water purification: Evaporation is used to remove impurities from water.
- Food processing: Evaporation is used to preserve food by removing moisture.
What is the main factor that influences evaporation rate?
+The main factor that influences evaporation rate is temperature. Increasing the temperature can accelerate evaporation, while decreasing the temperature can slow it down.
How can I enhance evaporation?
+Evaporation can be enhanced by increasing the temperature, reducing humidity, increasing air flow, and increasing the surface area of the liquid.
What are the applications of easy evaporation?
+Easy evaporation has numerous applications in various fields, including chemistry, physics, and engineering. Some examples include distillation, crystallization, drying, water purification, and food processing.