Acs Citation Style

The ACS (American Chemical Society) citation style is a widely used format for citing sources in the field of chemistry and other sciences. It is known for its simplicity and clarity, making it easier for authors to properly credit the work of others and for readers to locate referenced sources. The ACS style is detailed in the "ACS Style Guide," which provides comprehensive guidelines on how to format citations, references, and other aspects of scientific writing.
ACS Citation Style Overview
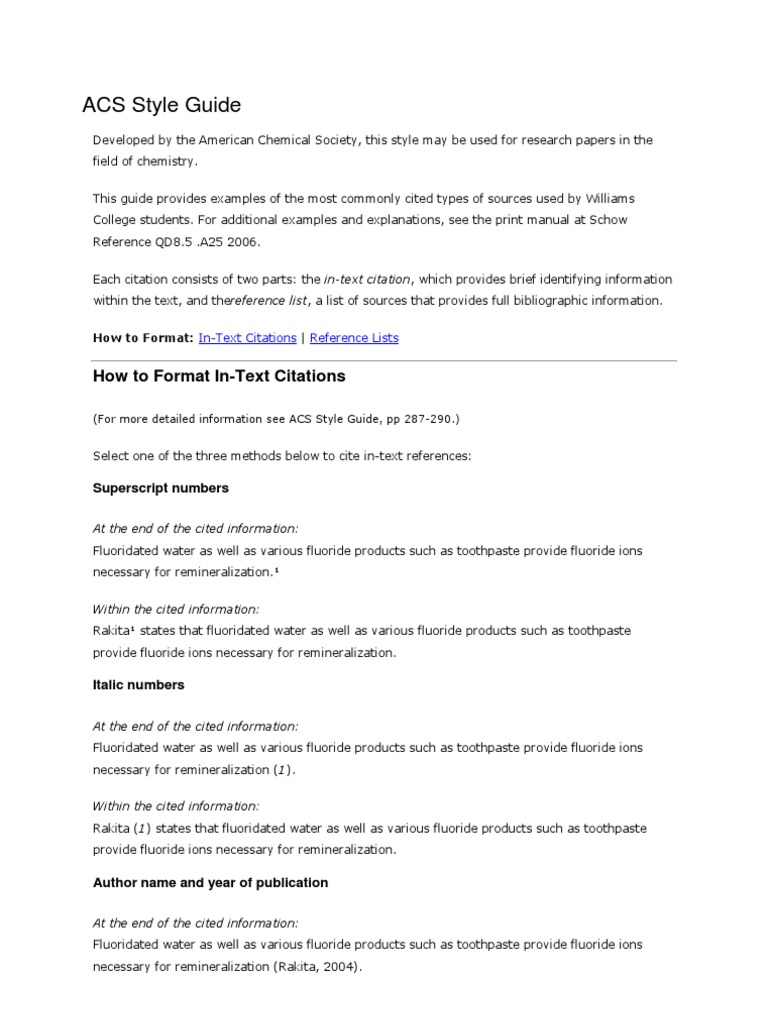
The ACS citation style involves citing sources in the text using a combination of superscript numbers and a list of references at the end of the document. In-text citations are numbered sequentially as they appear in the text, and these numbers correspond to the full citations provided in the reference list. The reference list is organized in the order that the sources appear in the text, not alphabetically by author.
In-Text Citations
In the ACS style, in-text citations are indicated by superscript numbers. These numbers are placed at the end of the sentence or clause that refers to the source, and they should be included after any punctuation marks, except for a dash. For example, if an author is referencing a study on the effects of climate change, the citation might look like this: The study found significant impacts on global temperatures1. If there are multiple citations in one sentence, they are separated by commas: The study found significant impacts on global temperatures1,2.
Reference List
The reference list provides the full citation information for each source cited in the text. The format of the reference list entries varies depending on the type of source (e.g., journal article, book, chapter in an edited book). For a journal article, the reference typically includes the authors’ names, the title of the article, the journal title, the year of publication, and the volume and page numbers. For example:
| Component | Format |
|---|---|
| Authors | Last name, Initials |
| Article Title | Title case, no quotation marks |
| Journal Title | Abbreviated title (if applicable), italicized |
| Year | Year of publication |
| Volume and Page Numbers | Volume number (italicized), page range |

Example of a journal article reference: Doe, J. T.; Smith, J. M. Synthesis of Novel Compounds. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020, 142 (10), 4567–4572.
Types of Sources

The ACS style provides guidelines for citing a wide range of source types, including but not limited to journal articles, books, chapters in edited books, conference presentations, and web pages. Each type of source has a specific format that must be followed to ensure consistency and clarity.
Journal Articles
Journal articles are a primary source of information in scientific research. When citing a journal article, it is essential to include all the necessary details, such as the authors’ names, article title, journal title (abbreviated if applicable), year of publication, volume number (italicized), and page range.
Books
For books, the citation includes the authors’ or editors’ names, book title (italicized), publisher, city of publication, and year of publication. If a specific chapter is being referenced, the chapter title and authors (if different from the book authors) should also be included.
Conference Presentations
Conference presentations, including papers and posters, are cited with the authors’ names, title of the presentation (in title case), name of the conference (italicized), location of the conference, and dates of the conference.
Technical Specifications and Performance Analysis

When discussing technical specifications and analyzing the performance of materials, devices, or processes, it is crucial to adhere strictly to the ACS citation style to maintain the integrity and reproducibility of the research. This includes citing sources for any data, methods, or previous findings that are referenced or built upon in the study.
Data Presentation
Data should be presented in a clear and concise manner, using tables, figures, and schemes as appropriate. Each table, figure, or scheme must be numbered and have a descriptive caption. Sources of the data should be cited in the caption or in the text, following the ACS in-text citation guidelines.
| Data Type | Presentation Guidelines |
|---|---|
| Numerical Data | Present in tables or as part of the text, with appropriate units and precision |
| Graphical Data | Present in figures, with clear labels and legends |
| Spectral Data | Present in schemes or figures, with detailed descriptions of the conditions under which the spectra were obtained |
What are the key components of an ACS-style reference for a journal article?
+The key components include the authors' names, article title, journal title (abbreviated if applicable), year of publication, volume number (italicized), and page range.
How should in-text citations be formatted according to the ACS style?
+In-text citations are indicated by superscript numbers placed at the end of the sentence or clause, after any punctuation marks except for a dash. Multiple citations in one sentence are separated by commas.
The ACS citation style is designed to facilitate clear communication of scientific information, ensuring that credits are given where due and that readers can easily find the sources referenced in a document. By following the guidelines outlined in the “ACS Style Guide,” authors can contribute to the integrity and accessibility of scientific literature.



