What Is The Freezing Point Of Water
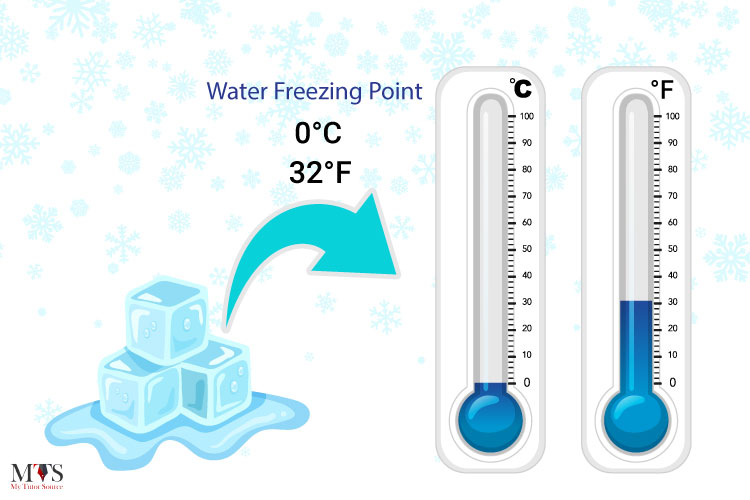
The freezing point of water is a fundamental physical constant that has been extensively studied and measured. At standard atmospheric pressure, the freezing point of water is defined as 0 degrees Celsius (°C) or 32 degrees Fahrenheit (°F). This temperature is the point at which water changes state from a liquid to a solid, forming ice. The freezing point of water is a critical parameter in various fields, including chemistry, physics, biology, and engineering, as it affects the behavior and properties of water in different environments.
Physical Properties of Water at Freezing Point

At the freezing point, water exhibits unique physical properties that distinguish it from other substances. The density of water at 0°C is approximately 0.9998 grams per milliliter (g/mL), which is slightly less than its density at room temperature. The heat capacity of water at freezing point is also an important property, as it affects the energy required to change the temperature of water. The heat capacity of water at 0°C is approximately 4.184 joules per gram per degree Celsius (J/g°C).
Factors Affecting Freezing Point of Water
The freezing point of water can be affected by various factors, including pressure, dissolved substances, and purification methods. At higher pressures, the freezing point of water decreases, while at lower pressures, it increases. Dissolved substances, such as salts or sugars, can also lower the freezing point of water, a phenomenon known as freezing-point depression. The purification method used to obtain water can also affect its freezing point, as impurities can alter the physical properties of water.
| Factor | Effect on Freezing Point |
|---|---|
| Pressure (increased) | Decrease in freezing point |
| Dissolved substances (e.g., salts, sugars) | Decrease in freezing point (freezing-point depression) |
| Purification method (e.g., distillation, filtration) | Potential alteration of freezing point due to impurities |

The freezing point of water has been measured with high accuracy using various techniques, including thermometry and calorimetry. These measurements have been refined over time, and the current definition of the freezing point of water is based on the International Temperature Scale of 1990 (ITS-90). The ITS-90 defines the freezing point of water as 0°C, which is equivalent to 273.15 kelvins (K) or 32°F.
Practical Applications of Freezing Point of Water

The freezing point of water has numerous practical applications in various fields, including engineering, biology, and environmental science. For example, understanding the freezing point of water is essential for designing cooling systems, such as refrigeration and air conditioning systems. In biology, the freezing point of water is critical for understanding the behavior of living organisms in cold environments, such as cryopreservation and frost tolerance. In environmental science, the freezing point of water is important for understanding climate change and its effects on water resources and ecosystems.
Future Implications of Freezing Point of Water
The freezing point of water will continue to play a critical role in various scientific and industrial applications. As climate change continues to affect global temperatures and water resources, understanding the freezing point of water will be essential for predicting and mitigating its impacts. Additionally, advances in materials science and nanotechnology may lead to the development of new materials and technologies that can manipulate the freezing point of water, potentially revolutionizing energy storage and water treatment applications.
What is the freezing point of water at high pressures?
+The freezing point of water at high pressures is lower than 0°C. For example, at a pressure of 1000 atmospheres (atm), the freezing point of water is approximately -20°C. This is because the increased pressure reduces the energy required for water molecules to form a crystal lattice, allowing them to freeze at a lower temperature.
How does the freezing point of water affect climate modeling?
+The freezing point of water is a critical parameter in climate modeling, as it affects the behavior of water in the atmosphere and oceans. Accurate predictions of the freezing point of water are essential for modeling sea ice formation and glacier dynamics, which are critical components of the global climate system. Small changes in the freezing point of water can have significant impacts on climate model predictions, highlighting the importance of accurate measurements and understanding of this physical constant.