What Is Semi Conservative Replication? Expert Guide
Semi-conservative replication is a fundamental process in molecular biology that describes the mechanism by which DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) makes a copy of itself during cell division. This process is crucial for the transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. The term "semi-conservative" was coined because the resulting DNA molecules are composed of one old strand (conserved from the original molecule) and one newly synthesized strand.
Understanding DNA Structure and Replication

DNA is a double-stranded helix made up of nucleotides, each containing a sugar molecule called deoxyribose, a phosphate group, and one of four nitrogenous bases: adenine (A), guanine (G), cytosine ©, and thymine (T). The sequence of these bases determines the genetic code. The double helix model of DNA, proposed by James Watson and Francis Crick in 1953, suggests that the two strands are complementary, with adenine pairing with thymine (A-T) and guanine pairing with cytosine (G-C). This complementarity is the basis for DNA replication.
The Semi-Conservative Replication Process
The process of semi-conservative replication involves several key steps: 1. Initiation: The double helix is unwound at a specific region called the origin of replication, and an enzyme called helicase unwinds the double helix structure. 2. Unwinding and Binding: As the double helix is unwound, another enzyme called primase adds short RNA primers to the template strands at specific regions called the primer binding sites. 3. Synthesis: DNA polymerase, an enzyme that synthesizes DNA, reads the template strands and matches the incoming nucleotides to the base pairing rules (A-T and G-C). It then links these nucleotides together, forming a new complementary strand. 4. Elongation: This process continues as the replication fork moves along the DNA molecule, with DNA polymerase continuously adding nucleotides to the growing strand. 5. Ligation: Once the synthesis is complete, an enzyme called DNA ligase seals the gaps between the nucleotides, forming a continuous strand.
| Step in Replication | Description |
|---|---|
| Initiation | Beginning of the replication process where the DNA double helix is unwound. |
| Unwinding and Binding | Helicase unwinds DNA, and primase adds RNA primers to template strands. |
| Synthesis | DNA polymerase synthesizes new DNA strands by adding nucleotides to the template strands. |
| Elongation | Continuation of DNA synthesis as the replication fork moves along the DNA. |
| Ligation | DNA ligase seals the gaps between nucleotides, completing the replication process. |

Evidence for Semi-Conservative Replication

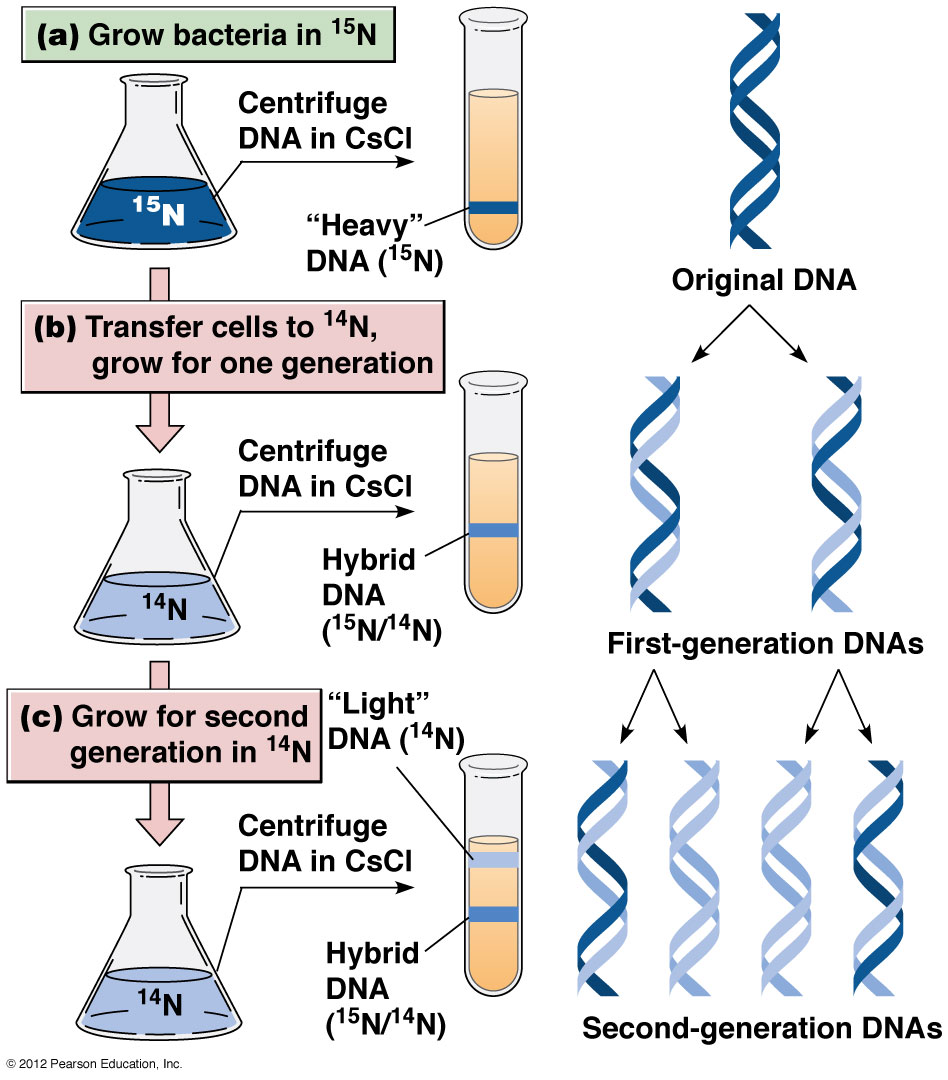
The semi-conservative model of DNA replication was experimentally confirmed by the Meselson-Stahl experiment in 1958. Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl used Escherichia coli bacteria and grew them in a medium containing a heavy isotope of nitrogen (¹⁵N) to label their DNA. They then transferred the bacteria to a medium containing a light isotope of nitrogen (¹⁴N) and allowed them to replicate. By using density gradient centrifugation to separate the DNA based on density, they observed that after one generation, the DNA was half-heavy and half-light, indicating that each new DNA molecule contained one old strand (heavy) and one newly synthesized strand (light). This result supported the semi-conservative replication model.
Importance of Semi-Conservative Replication
The semi-conservative mechanism of DNA replication has several important implications: - Genetic Continuity: It ensures that the genetic information is passed on accurately from one generation of cells to the next. - Evolutionary Adaptation: Errors during replication can lead to mutations, which are a driving force behind evolutionary changes. - DNA Repair Mechanisms: Understanding how DNA replicates helps in comprehending the mechanisms by which cells repair damaged DNA, which is crucial for preventing mutations that could lead to diseases like cancer.
What is the difference between semi-conservative and conservative DNA replication?
+In semi-conservative replication, each new DNA molecule contains one old strand and one newly synthesized strand. In contrast, conservative replication would result in one DNA molecule being entirely new and the other remaining entirely old, which is not supported by experimental evidence.
Why is the Meselson-Stahl experiment significant?
+The Meselson-Stahl experiment provided conclusive evidence for the semi-conservative model of DNA replication, confirming the predictions made by Watson and Crick's double helix model. It demonstrated how genetic material is replicated and passed on to daughter cells.
In conclusion, semi-conservative replication is a fundamental biological process that ensures the accurate transmission of genetic information from one generation of cells to the next. Understanding this process is essential for appreciating the mechanisms of genetic inheritance, the basis of evolutionary change, and the importance of DNA repair in maintaining genome stability.



