What Is Cooking Soda Chemical Formula? Easy Answers
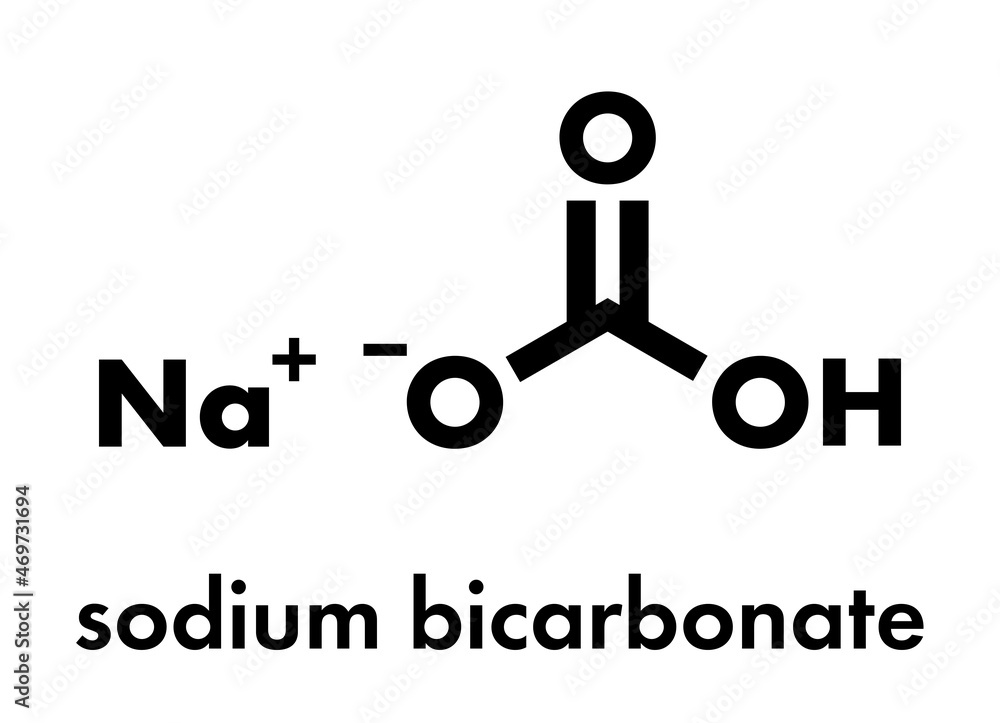
Cooking soda, also known as baking soda, is a chemical compound that has been used for centuries in various applications, including cooking, cleaning, and personal care. The chemical formula for cooking soda is NaHCO3, which stands for sodium bicarbonate. This compound is composed of one sodium (Na) atom, one hydrogen (H) atom, one carbon (C) atom, and three oxygen (O) atoms.
Chemical Structure and Properties

The chemical structure of cooking soda is based on a trigonal planar geometry, where the sodium atom is bonded to the bicarbonate ion (HCO3-). The bicarbonate ion is composed of a central carbon atom bonded to three oxygen atoms and one hydrogen atom. The chemical properties of cooking soda make it a weak base, which means it can neutralize acids and release carbon dioxide gas (CO2) in the process.
Chemical Reactions and Applications
Cooking soda is commonly used in baking as a leavening agent, where it releases carbon dioxide gas when it comes into contact with an acid, such as buttermilk or yogurt, and a liquid, such as water or milk. This reaction causes the dough or batter to rise, giving baked goods their light and fluffy texture. The chemical reaction is as follows: NaHCO3 + H+ → CO2 + H2O + Na+. Cooking soda is also used in cleaning and personal care products, such as toothpaste and antacids, due to its ability to neutralize acids and absorb odors.
| Chemical Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 84.0066 g/mol |
| Density | 2.2 g/cm3 |
| Melting Point | 50-100°C (122-212°F) |
| Boiling Point | Decomposes at 200°C (392°F) |
Industrial Applications and Production

Cooking soda is produced through the Solvay process, which involves the reaction of sodium chloride (NaCl) with ammonia (NH3) and carbon dioxide (CO2) to produce sodium bicarbonate (NaHCO3) and ammonium chloride (NH4Cl). The industrial production of cooking soda involves the mining of trona, a mineral that contains sodium bicarbonate, and the processing of the mineral to produce pure sodium bicarbonate.
Environmental and Health Implications
The production and use of cooking soda have minimal environmental and health implications, as it is a naturally occurring compound that is biodegradable and non-toxic. However, the mining of trona and the production of cooking soda can have environmental impacts, such as air and water pollution, if proper safety measures are not taken. Additionally, excessive consumption of cooking soda can have health implications, such as gastrointestinal problems and electrolyte imbalances.
The following are some key points to consider when using cooking soda:
- Cooking soda is a weak base that can neutralize acids and release carbon dioxide gas.
- It is commonly used in baking, cleaning, and personal care products.
- The production of cooking soda involves the mining of trona and the processing of the mineral to produce pure sodium bicarbonate.
- The environmental and health implications of cooking soda are minimal, but excessive consumption can have negative effects.
What is the chemical formula for cooking soda?
+The chemical formula for cooking soda is NaHCO3, which stands for sodium bicarbonate.
What are the common uses of cooking soda?
+Cooking soda is commonly used in baking, cleaning, and personal care products, such as toothpaste and antacids.
What are the environmental and health implications of cooking soda?
+The production and use of cooking soda have minimal environmental and health implications, but excessive consumption can have negative effects, such as gastrointestinal problems and electrolyte imbalances.
In conclusion, cooking soda is a versatile compound with a wide range of applications, from cooking and cleaning to personal care and industrial uses. Its chemical properties make it a weak base that can neutralize acids and release carbon dioxide gas, and its production involves the mining of trona and the processing of the mineral to produce pure sodium bicarbonate. While the environmental and health implications of cooking soda are minimal, excessive consumption can have negative effects, and proper safety measures should be taken to minimize its impact on the environment and human health.



