What Is A Scale For A Map
A scale for a map is a ratio or proportion that represents the relationship between the size of an object or feature on the map and its actual size in the real world. It is a critical component of cartography, as it allows users to understand the spatial relationships between different features and to measure distances and sizes accurately. The scale is usually represented as a ratio, such as 1:10,000 or 1:50,000, where the first number represents the size of the object on the map and the second number represents the actual size of the object in the real world.
For example, a map with a scale of 1:10,000 means that one unit of measurement on the map (such as one centimeter) represents 10,000 units of measurement in the real world (such as 10,000 centimeters or 100 meters). This allows users to calculate the actual distance between two points on the map by measuring the distance between them on the map and multiplying it by the scale factor. Scales can be represented in different ways, including as a ratio, a graphic scale, or a written statement, and they can be used to create maps at a variety of scales, from small-scale maps that show large areas to large-scale maps that show small areas in great detail.
Types of Map Scales
There are several types of map scales, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. Small-scale maps, such as those used for navigation or to show the relationship between different regions, typically have a scale of 1:100,000 or smaller. These maps are useful for showing the overall layout of an area, but they may not provide enough detail to be useful for navigation or other purposes. Medium-scale maps, such as those used for hiking or biking, typically have a scale of 1:25,000 to 1:50,000. These maps provide a good balance between detail and overview, and are often used for recreational activities. Large-scale maps, such as those used for engineering or construction projects, typically have a scale of 1:1,000 to 1:5,000. These maps provide a high level of detail, and are often used for precise measurements and calculations.
Understanding Map Scales
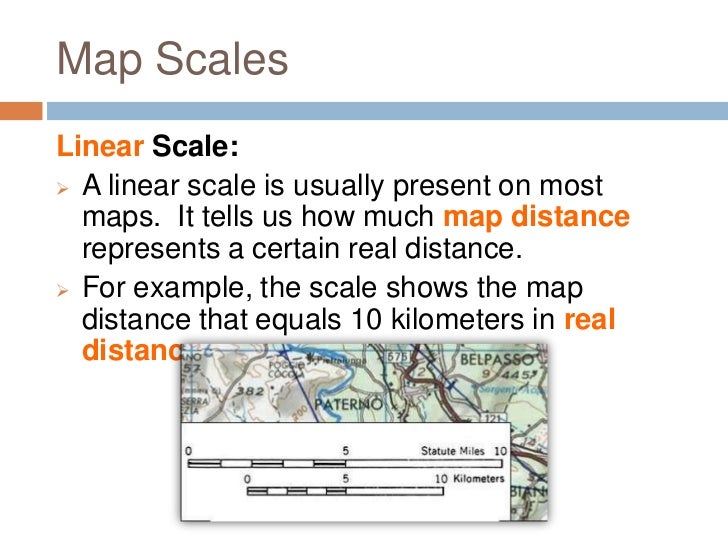
To understand a map scale, it is essential to know how to read and interpret it. The scale is usually shown on the map as a ratio, such as 1:10,000, or as a graphic scale, which is a line or bar that shows the relationship between distances on the map and actual distances. To use the scale, simply measure the distance between two points on the map, and then multiply that distance by the scale factor to get the actual distance. For example, if the scale is 1:10,000 and the distance between two points on the map is 5 centimeters, the actual distance would be 50,000 centimeters or 500 meters.
| Scale | Description |
|---|---|
| 1:10,000 | Small-scale map, useful for navigation or showing relationships between regions |
| 1:25,000 | Medium-scale map, useful for hiking or biking |
| 1:1,000 | Large-scale map, useful for engineering or construction projects |

In addition to understanding the scale, it's also essential to consider other factors that can affect the accuracy and usefulness of a map. These include the projection used to create the map, which can affect the shape and size of features, and the resolution of the map, which can affect the level of detail shown. By considering these factors and understanding the scale of a map, users can get the most out of their maps and use them effectively for a variety of purposes.
Map Scale Applications

Map scales have a wide range of applications, from navigation and recreation to engineering and construction. Small-scale maps are often used for navigation, such as when driving or hiking, while medium-scale maps are often used for recreational activities, such as hiking or biking. Large-scale maps are often used for engineering or construction projects, such as building design or surveying. In addition to these applications, map scales can also be used for a variety of other purposes, such as urban planning, environmental monitoring, or emergency response.
For example, a city planner might use a large-scale map to design a new development, while a park ranger might use a medium-scale map to navigate trails and monitor wildlife habitats. An engineer might use a small-scale map to plan a new highway, while a surveyor might use a large-scale map to measure property boundaries. By using maps with the appropriate scale, professionals and individuals can get the information they need to make informed decisions and take effective action.
Map Scale Limitations
While map scales are essential for understanding and using maps, they also have some limitations. One of the main limitations is that maps can never be perfectly accurate, due to the distortions and approximations that are inherent in the mapping process. Additionally, maps can become outdated as new features are built or existing ones change, which can affect their usefulness. Finally, maps can be affected by the resolution and accuracy of the data used to create them, which can impact their overall quality and reliability.
- Map scales can affect the accuracy and usefulness of a map
- Maps can never be perfectly accurate due to distortions and approximations
- Maps can become outdated as new features are built or existing ones change
What is the purpose of a map scale?
+The purpose of a map scale is to provide a ratio or proportion that represents the relationship between the size of an object or feature on the map and its actual size in the real world. This allows users to understand the spatial relationships between different features and to measure distances and sizes accurately.
How do I read a map scale?
+To read a map scale, simply look for the ratio or proportion that is shown on the map, such as 1:10,000. This means that one unit of measurement on the map represents 10,000 units of measurement in the real world. You can use this ratio to calculate the actual distance between two points on the map by measuring the distance between them on the map and multiplying it by the scale factor.
In conclusion, map scales are a crucial component of cartography, and are used to represent the relationship between the size of an object or feature on a map and its actual size in the real world. By understanding map scales and how to use them, individuals and professionals can get the most out of their maps and use them effectively for a variety of purposes. Whether you’re a navigator, a planner, or an engineer, knowing how to read and interpret a map scale is an essential skill that can help you achieve your goals and make informed decisions.



