What Is A Mac Address
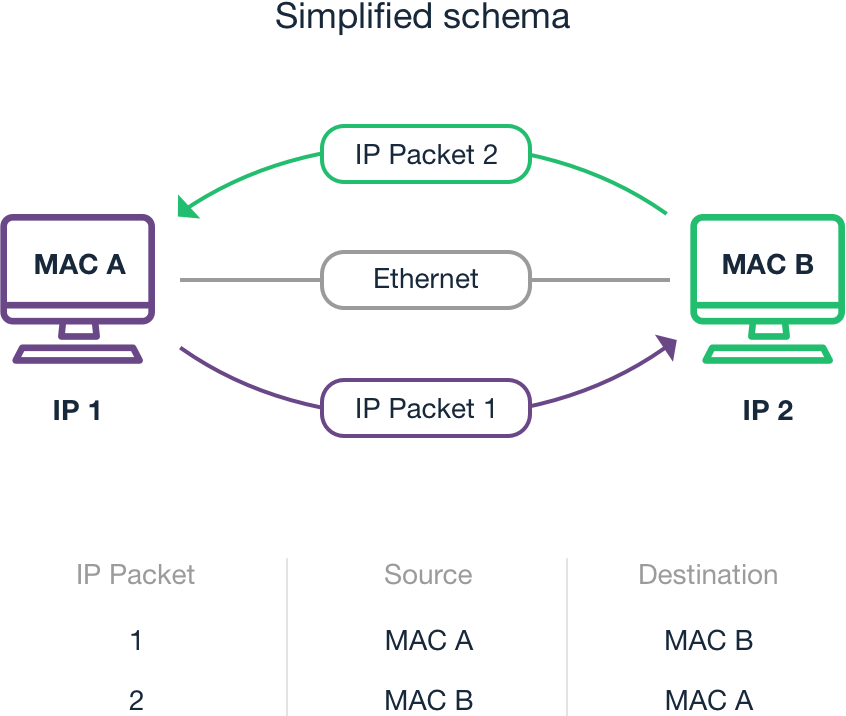
A Media Access Control (MAC) address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in the data link layer of a network segment. It is a 48-bit or 64-bit address that is usually represented as a six-part hexadecimal number, separated by colons or dashes. The MAC address is used to identify a device at the data link layer of a network, which is the layer that controls the interaction between devices on the same network.
The MAC address is stored in the read-only memory (ROM) of the network interface controller (NIC) and is used to identify the device at the data link layer of a network. It is an essential component of the network protocol suite, as it allows devices to communicate with each other and to identify the source and destination of data packets. The MAC address is also used in various network protocols, such as the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP), which maps IP addresses to MAC addresses, and the Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP), which assigns IP addresses to devices on a network.
Structure of a MAC Address

A MAC address is typically represented as a six-part hexadecimal number, separated by colons or dashes. The structure of a MAC address can be broken down into several parts, including the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), the vendor code, and the interface serial number. The OUI is a 24-bit number that identifies the manufacturer of the network interface controller (NIC), while the vendor code is a 16-bit number that identifies the specific model of the NIC. The interface serial number is a 24-bit number that is unique to each device.
The following is an example of a MAC address: 00:11:22:33:44:55. In this example, the first three parts (00:11:22) represent the OUI, which identifies the manufacturer of the NIC. The last three parts (33:44:55) represent the interface serial number, which is unique to each device. The vendor code is not explicitly represented in this example, but it is typically embedded in the OUI.
Types of MAC Addresses
There are two main types of MAC addresses: unicast and multicast. A unicast MAC address is a unique address that is assigned to a single device on a network, while a multicast MAC address is a shared address that is assigned to a group of devices on a network. Multicast MAC addresses are used to send data packets to multiple devices on a network, rather than to a single device.
In addition to unicast and multicast MAC addresses, there are also several other types of MAC addresses, including broadcast MAC addresses and locally administered MAC addresses. A broadcast MAC address is a special type of MAC address that is used to send data packets to all devices on a network, rather than to a single device or group of devices. A locally administered MAC address is a type of MAC address that is assigned by the network administrator, rather than by the manufacturer of the NIC.
| Type of MAC Address | Description |
|---|---|
| Unicast MAC Address | A unique address assigned to a single device on a network |
| Multicast MAC Address | A shared address assigned to a group of devices on a network |
| Broadcast MAC Address | A special type of MAC address used to send data packets to all devices on a network |
| Locally Administered MAC Address | A type of MAC address assigned by the network administrator |

How MAC Addresses are Used
MAC addresses are used in a variety of ways, including to identify devices on a network, to route data packets, and to provide security. When a device sends a data packet on a network, it includes its MAC address in the packet header, which allows the packet to be routed to the correct destination. MAC addresses are also used by network devices, such as routers and switches, to forward data packets to the correct destination.
In addition to routing data packets, MAC addresses are also used to provide security on a network. For example, a network administrator can use MAC address filtering to control which devices are allowed to access a network. By configuring a network device to only allow devices with specific MAC addresses to access the network, the administrator can prevent unauthorized devices from accessing the network.
MAC Address Filtering
MAC address filtering is a security technique that is used to control which devices are allowed to access a network. By configuring a network device to only allow devices with specific MAC addresses to access the network, the administrator can prevent unauthorized devices from accessing the network. MAC address filtering can be used in a variety of situations, including to prevent unauthorized devices from accessing a wireless network or to control which devices are allowed to access a sensitive area of a network.
The following are the steps to configure MAC address filtering on a network device:
- Obtain the MAC address of the device that you want to allow or block
- Configure the network device to use MAC address filtering
- Add the MAC address of the device to the list of allowed or blocked devices
- Save the changes to the network device configuration
What is a MAC address?
+A MAC address is a unique identifier assigned to a network interface controller (NIC) for use as a network address in the data link layer of a network segment.
How is a MAC address structured?
+A MAC address is typically represented as a six-part hexadecimal number, separated by colons or dashes. The structure of a MAC address can be broken down into several parts, including the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI), the vendor code, and the interface serial number.
What is MAC address filtering?
+MAC address filtering is a security technique that is used to control which devices are allowed to access a network. By configuring a network device to only allow devices with specific MAC addresses to access the network, the administrator can prevent unauthorized devices from accessing the network.
Related Terms:
- mac address is also called
- example of a mac address



