What Are Polarization-Sensitive Plasmonic Particles?
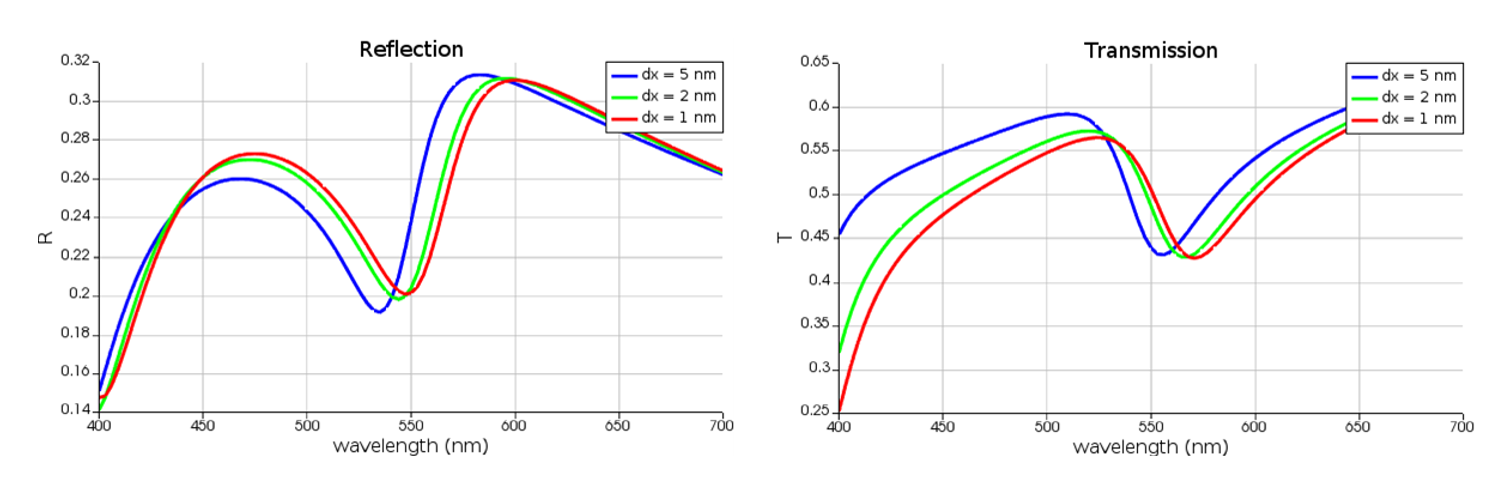
Polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles are a class of nanoparticles that exhibit unique optical properties due to their ability to manipulate light at the nanoscale. These particles are typically made of noble metals, such as gold or silver, and are designed to interact with light in a way that is sensitive to the polarization state of the incident light. The polarization state of light refers to the orientation of the electric field vector of the light wave, and plasmonic particles can be engineered to respond differently to different polarization states.
The unique properties of polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles arise from the interaction between the incident light and the free electrons at the surface of the particle. When light hits the particle, it causes the free electrons to oscillate, creating a collective oscillation known as a plasmon. The properties of the plasmon, such as its frequency and amplitude, depend on the shape, size, and composition of the particle, as well as the polarization state of the incident light. By carefully designing the particle's geometry and material properties, researchers can create particles that exhibit specific polarization-sensitive properties, such as polarization-dependent scattering or polarization-dependent absorption.
Principles of Polarization-Sensitive Plasmonic Particles
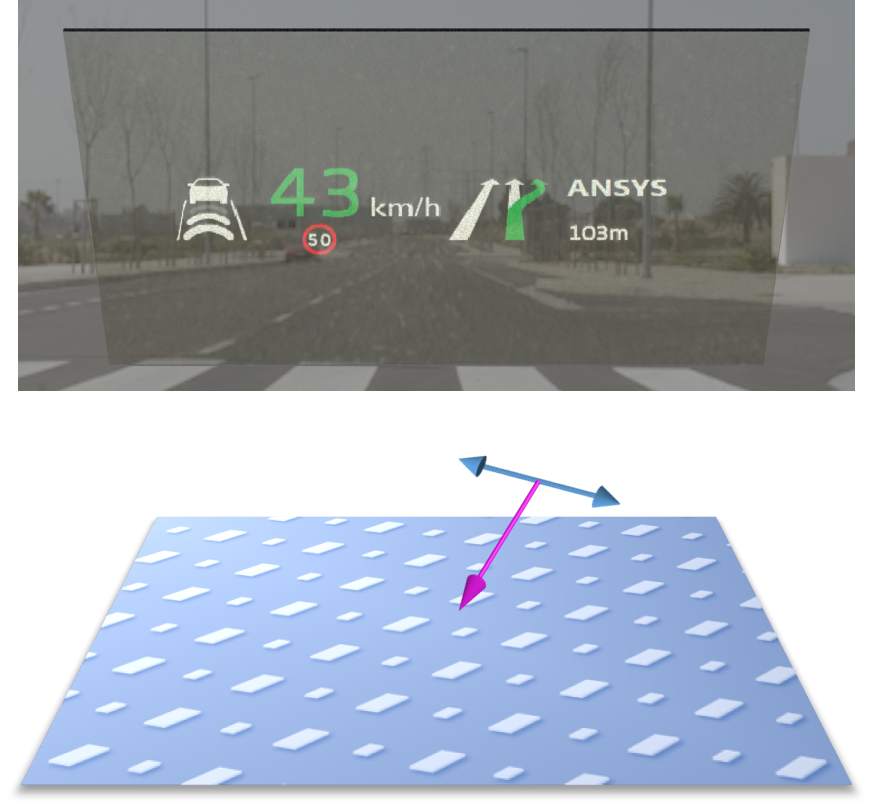
The principles underlying the behavior of polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles can be understood by considering the electromagnetic response of the particle to incident light. The particle's response is governed by the Maxwell equations, which describe the interaction between the electromagnetic field and the free electrons at the surface of the particle. By solving the Maxwell equations for a given particle geometry and material composition, researchers can predict the particle's optical properties, including its polarization-sensitive behavior.
A key aspect of polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles is their ability to exhibit anisotropy, meaning that their optical properties depend on the direction of the incident light. This anisotropy can be achieved through the use of particles with non-spherical shapes, such as nanorods or nanoplates, which can exhibit different optical properties depending on the orientation of the incident light. Alternatively, particles with spherical shapes can be designed to exhibit anisotropy through the use of Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR) effects, which can be sensitive to the polarization state of the incident light.
Types of Polarization-Sensitive Plasmonic Particles
There are several types of polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles that have been developed, each with unique properties and applications. Some examples include:
- Nanorods: These particles have a rod-like shape and can exhibit polarization-dependent scattering or absorption due to their anisotropic shape.
- Nanoplates: These particles have a plate-like shape and can exhibit polarization-dependent optical properties due to their anisotropic shape.
- Janus particles: These particles have a spherical shape but are composed of two different materials, which can exhibit different optical properties depending on the polarization state of the incident light.
- Core-shell particles: These particles have a spherical shape and are composed of a core material surrounded by a shell material, which can exhibit different optical properties depending on the polarization state of the incident light.
| Particle Type | Polarization-Sensitive Property |
|---|---|
| Nanorods | Polarization-dependent scattering |
| Nanoplates | Polarization-dependent absorption |
| Janus particles | Polarization-dependent optical activity |
| Core-shell particles | Polarization-dependent SPR effects |

Applications of Polarization-Sensitive Plasmonic Particles

Polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles have a wide range of potential applications, including biomedical imaging, sensing, and optical communication. In biomedical imaging, these particles can be used to create high-contrast images of tissues or cells, allowing for early disease detection and diagnosis. In sensing applications, these particles can be used to detect specific biomolecules or chemicals, allowing for rapid and sensitive detection of diseases or environmental pollutants. In optical communication, these particles can be used to create ultra-compact and ultra-fast optical switches, allowing for high-speed data transmission and processing.
Some of the key benefits of using polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles include their high sensitivity, high specificity, and compact size. These particles can be designed to exhibit high sensitivity to specific polarization states, allowing for precise control over their optical properties. Additionally, these particles can be designed to exhibit high specificity, allowing for selective detection or imaging of specific targets. Finally, these particles can be designed to be compact and ultra-small, allowing for integration into a wide range of devices and systems.
Future Directions and Challenges
While polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles have shown great promise for a wide range of applications, there are still several challenges and future directions that need to be addressed. Some of the key challenges include:
- Scalability: Currently, the synthesis and fabrication of polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles can be time-consuming and expensive. Developing scalable and cost-effective methods for producing these particles is essential for their widespread adoption.
- Stability: Polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles can be prone to degradation or instability, which can affect their optical properties and performance. Developing strategies for improving the stability and durability of these particles is essential for their practical applications.
- Toxicity: Some polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles can be toxic or hazardous, which can limit their use in biomedical or environmental applications. Developing non-toxic and biocompatible particles is essential for their safe and effective use.
What are the advantages of using polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles?
+The advantages of using polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles include their high sensitivity, high specificity, and compact size. These particles can be designed to exhibit high sensitivity to specific polarization states, allowing for precise control over their optical properties. Additionally, these particles can be designed to exhibit high specificity, allowing for selective detection or imaging of specific targets.
What are the potential applications of polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles?
+The potential applications of polarization-sensitive plasmonic particles include biomedical imaging, sensing, and optical communication. In biomedical imaging, these particles can be used to create high-contrast images of tissues or cells, allowing for early disease detection and diagnosis. In sensing applications, these particles can be used to detect specific biomolecules or chemicals, allowing for rapid and sensitive detection of diseases or environmental pollutants.



