Stores Material Such As Nutrients

The human body is composed of various systems that work together to maintain overall health and function. One of the essential systems is the digestive system, which is responsible for breaking down food into nutrients that can be absorbed and utilized by the body. The digestive system is made up of several organs, including the stomach, small intestine, and large intestine, each playing a crucial role in the digestion and absorption of nutrients. The liver, pancreas, and gallbladder also play important roles in the digestive process, producing enzymes, bile, and other substances that help to break down food into nutrients.
Digestion and Absorption of Nutrients
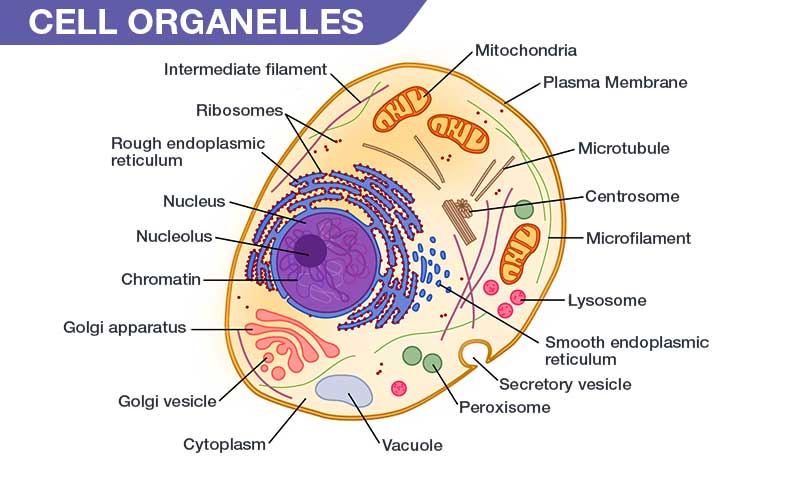
The process of digestion and absorption of nutrients is complex and involves several stages. First, food is ingested and broken down into smaller particles by the teeth and tongue. The food then passes through the esophagus and into the stomach, where it is mixed with stomach acid and digestive enzymes that break down proteins and fats. The partially digested food then enters the small intestine, where most of the nutrient absorption takes place. The walls of the small intestine are lined with finger-like projections called villi, which increase the surface area for absorption. The nutrients are then absorbed into the bloodstream and carried to the liver for processing and distribution to the rest of the body.
Role of the Liver in Nutrient Storage
The liver plays a crucial role in the storage of nutrients, particularly glycogen, which is a complex carbohydrate made up of glucose molecules. The liver stores glycogen in the form of glycogen granules, which can be broken down into glucose and released into the bloodstream when energy is needed. The liver also stores vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin B12 and iron, which are essential for various bodily functions. In addition, the liver produces bile, which helps to emulsify fats and facilitate their absorption in the small intestine.
| Nutrient | Storage Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Glycogen | Liver | Energy storage |
| Vitamin B12 | Liver | Nervous system function |
| Iron | Liver | Oxygen transport |
| Fats | Adipose tissue | Energy storage |
Other Organs Involved in Nutrient Storage

In addition to the liver, other organs such as the pancreas, kidneys, and adipose tissue also play important roles in nutrient storage and regulation. The pancreas produces hormones such as insulin and glucagon, which help to regulate blood sugar levels and facilitate the storage and release of glucose. The kidneys help to regulate electrolyte levels and maintain acid-base balance, while adipose tissue stores fat and releases it when energy is needed.
Regulation of Nutrient Storage and Release
The regulation of nutrient storage and release is a complex process that involves the coordinated action of multiple organs and hormones. The hypothalamus, a region of the brain, plays a crucial role in regulating energy homeostasis and nutrient storage by controlling the release of hormones such as insulin and glucagon. The adrenal glands also produce hormones such as cortisol and adrenaline, which help to regulate blood sugar levels and facilitate the release of glucose during times of stress.
- Insulin: regulates blood sugar levels and facilitates glucose uptake in cells
- Glucagon: stimulates the release of glucose from stored glycogen
- Cortisol: regulates blood sugar levels and facilitates the release of glucose during times of stress
- Adrenaline: stimulates the release of glucose from stored glycogen and increases blood sugar levels
What is the main function of the liver in nutrient storage?
+The main function of the liver in nutrient storage is to store glycogen, which is a complex carbohydrate made up of glucose molecules. The liver also stores vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin B12 and iron, which are essential for various bodily functions.
Which hormone regulates blood sugar levels and facilitates glucose uptake in cells?
+Insulin is the hormone that regulates blood sugar levels and facilitates glucose uptake in cells. It is produced by the pancreas and plays a crucial role in maintaining energy homeostasis and overall health.
Related Terms:
- which organelles store food



