Sildenafil Vs Vardenafil
Sildenafil and vardenafil are two of the most commonly prescribed medications for the treatment of erectile dysfunction (ED). Both belong to a class of drugs known as phosphodiesterase type 5 (PDE5) inhibitors, which work by increasing blood flow to the penis to help achieve and maintain an erection. Despite their similarities, sildenafil and vardenafil have distinct differences in terms of their pharmacology, efficacy, and side effect profiles.
Introduction to PDE5 Inhibitors
PDE5 inhibitors are a group of drugs that have revolutionized the treatment of ED. They work by inhibiting the action of phosphodiesterase type 5, an enzyme that breaks down cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) in the penis. cGMP is a key molecule involved in the relaxation of smooth muscle and the increased blood flow that occurs during an erection. By preventing the breakdown of cGMP, PDE5 inhibitors allow for increased blood flow to the penis, facilitating the achievement and maintenance of an erection.
Pharmacology of Sildenafil and Vardenafil
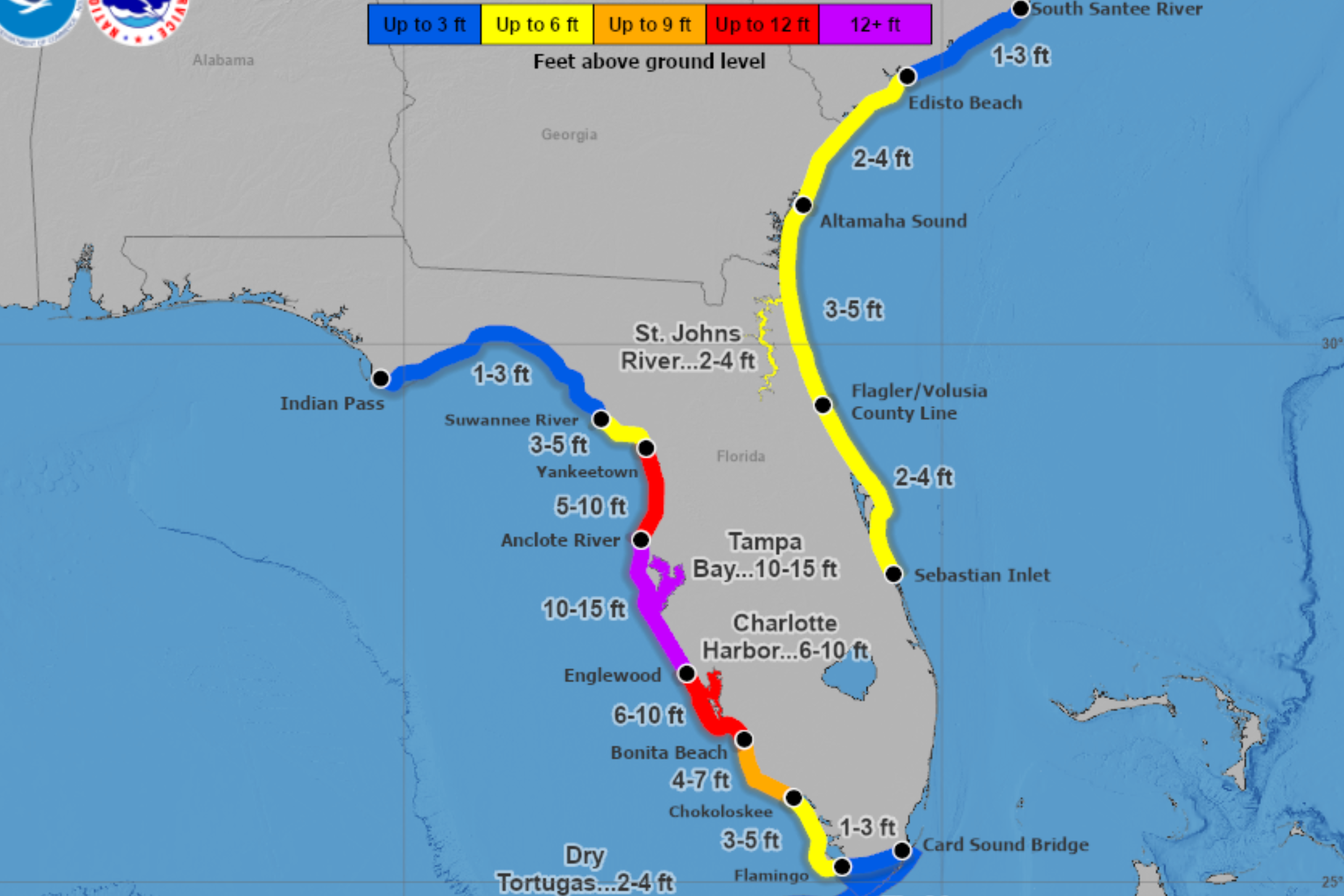
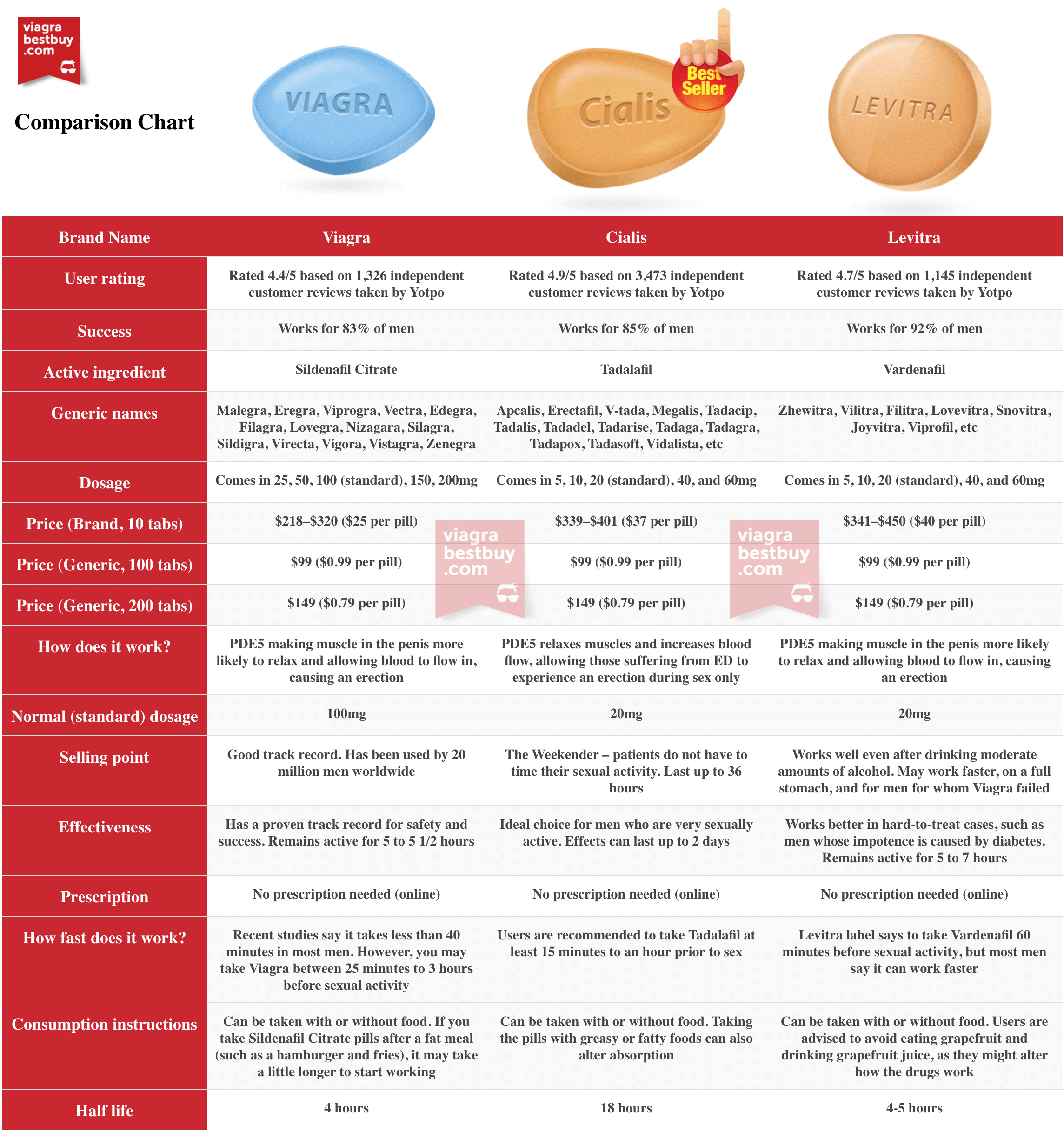
Sildenafil, commonly known by its brand name Viagra, was the first PDE5 inhibitor to be approved for the treatment of ED. It has a rapid onset of action, with peak plasma concentrations reached within 30-120 minutes after oral administration. Sildenafil has a half-life of approximately 3-4 hours, which means that its effects can last for up to 4-6 hours. Vardenafil, known by its brand name Levitra, has a similar pharmacokinetic profile to sildenafil, with a rapid onset of action and a half-life of approximately 4-5 hours.
| Medication | Onset of Action | Peak Plasma Concentration | Half-life |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sildenafil | 30-60 minutes | 30-120 minutes | 3-4 hours |
| Vardenafil | 30-60 minutes | 30-120 minutes | 4-5 hours |

Efficacy and Safety Profiles

Both sildenafil and vardenafil have been shown to be effective in the treatment of ED, with response rates ranging from 60-80% in clinical trials. However, the efficacy of these medications can be influenced by a variety of factors, including the severity of ED, the presence of underlying medical conditions, and the use of other medications. In terms of safety, both sildenafil and vardenafil have been associated with a range of side effects, including headache, flushing, and dyspepsia. However, vardenafil has been shown to have a slightly lower incidence of side effects compared to sildenafil.
Comparison of Side Effect Profiles
A study published in the Journal of Urology compared the side effect profiles of sildenafil and vardenafil in a group of men with ED. The study found that vardenafil was associated with a lower incidence of headache (12.1% vs 18.3%) and flushing (8.5% vs 12.1%) compared to sildenafil. However, the study also found that vardenafil was associated with a higher incidence of nasal congestion (6.2% vs 3.5%) compared to sildenafil.
- Sildenafil: headache (18.3%), flushing (12.1%), dyspepsia (10.5%)
- Vardenafil: headache (12.1%), flushing (8.5%), nasal congestion (6.2%)
What is the recommended dose of sildenafil and vardenafil?
+The recommended dose of sildenafil is 50mg, taken as needed, approximately 30-60 minutes before sexual activity. The recommended dose of vardenafil is 10mg, taken as needed, approximately 30-60 minutes before sexual activity.
Can sildenafil and vardenafil be taken with other medications?
+Sildenafil and vardenafil should not be taken with nitrates or other medications that contain nitrates, as this can increase the risk of hypotension. They should also be used with caution in patients taking alpha-blockers, as this can increase the risk of hypotension.
In conclusion, sildenafil and vardenafil are both effective medications for the treatment of ED, but they have distinct differences in terms of their pharmacology, efficacy, and side effect profiles. While sildenafil has a slightly faster onset of action, vardenafil has been shown to have a slightly lower incidence of side effects. Ultimately, the choice of medication will depend on individual patient factors, including the severity of ED, the presence of underlying medical conditions, and the use of other medications.
Future Implications

The development of new PDE5 inhibitors, such as tadalafil and avanafil, has further expanded the treatment options for ED. These medications have longer half-lives and can be taken with greater flexibility, making them a convenient option for patients. Additionally, the use of PDE5 inhibitors in combination with other medications, such as testosterone replacement therapy, may offer new treatment options for patients with ED.