Partial Pressure: Calculate Easily
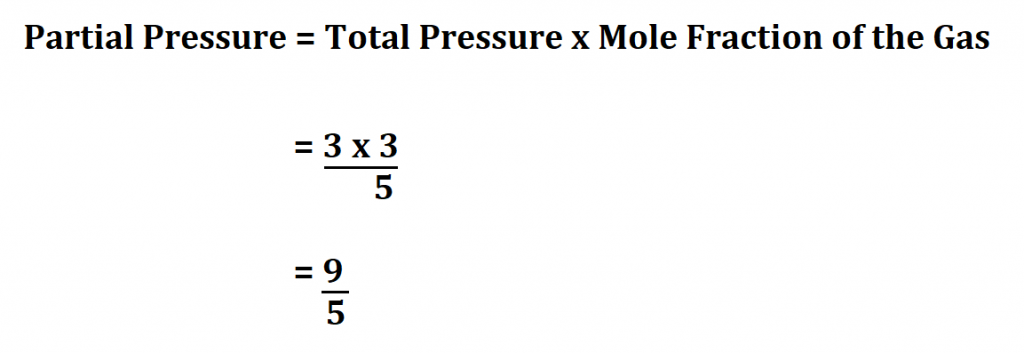
Partial pressure is a fundamental concept in chemistry and physics, particularly in the study of gases. It refers to the pressure exerted by a single component of a mixture of gases. Calculating partial pressure is crucial in various applications, including chemistry, biology, and engineering. In this article, we will delve into the concept of partial pressure, its significance, and provide a step-by-step guide on how to calculate it easily.
Understanding Partial Pressure
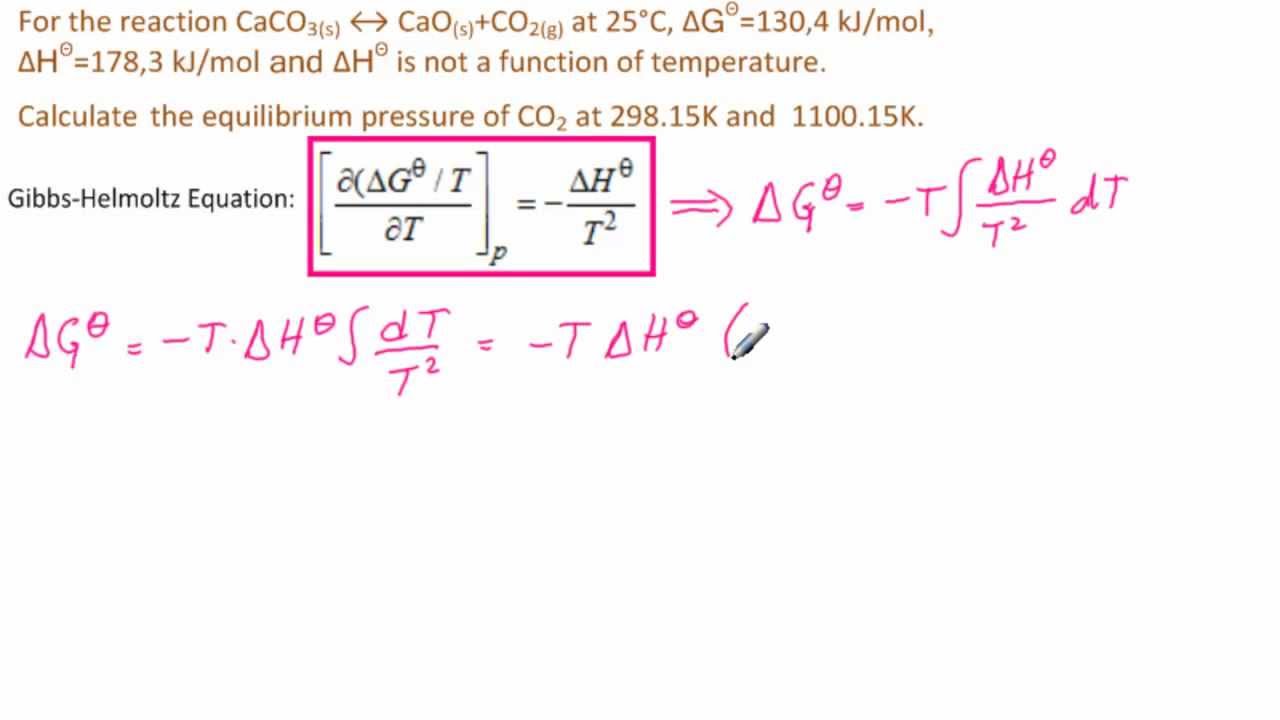
Partial pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a single component of a mixture of gases. It is a measure of the contribution of each gas to the total pressure of the mixture. The concept of partial pressure is based on the idea that each gas in a mixture behaves independently, and its pressure is proportional to its concentration. The partial pressure of a gas can be calculated using the formula: P = (n/V)RT, where P is the partial pressure, n is the number of moles of the gas, V is the volume of the container, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
Significance of Partial Pressure
The concept of partial pressure has numerous applications in various fields. In chemistry, partial pressure is used to calculate the equilibrium constant of a reaction, predict the direction of a reaction, and determine the solubility of gases in liquids. In biology, partial pressure is crucial in understanding the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the bloodstream. In engineering, partial pressure is used to design and optimize systems, such as air conditioning and refrigeration systems, that involve the compression and expansion of gases.
| Gas | Molecular Formula | Partial Pressure Formula |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen (O2) | O2 | P(O2) = (n(O2)/V)RT |
| Carbon Dioxide (CO2) | CO2 | P(CO2) = (n(CO2)/V)RT |
| Nitrogen (N2) | N2 | P(N2) = (n(N2)/V)RT |
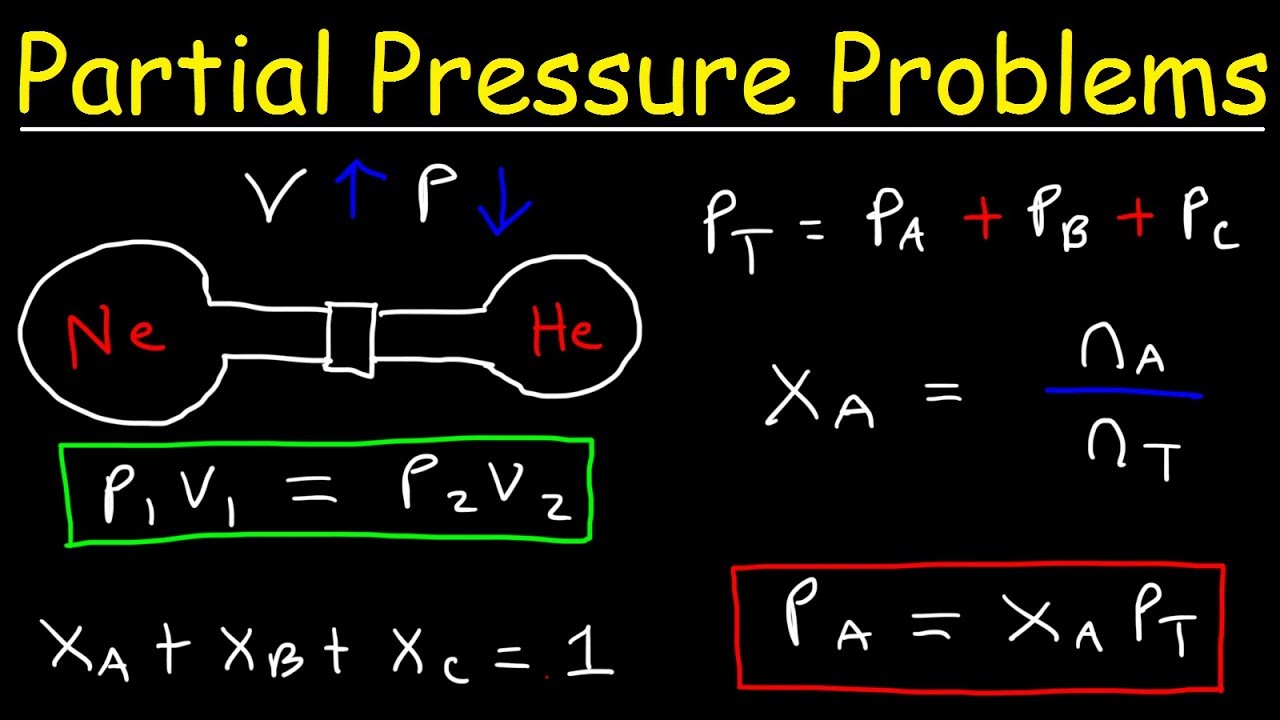
Calculating Partial Pressure Easily
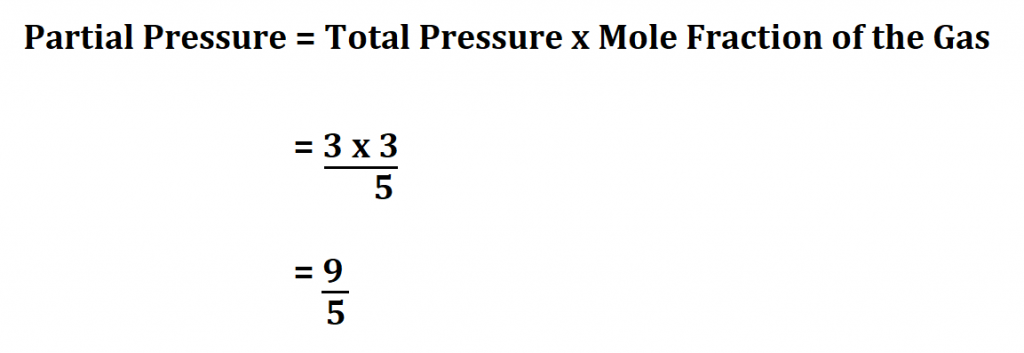
Calculating partial pressure can be straightforward if you follow these steps:
- Determine the number of moles of the gas (n) using the formula: n = PV/RT, where P is the total pressure, V is the volume of the container, R is the gas constant, and T is the temperature in Kelvin.
- Calculate the partial pressure of the gas (P) using the formula: P = (n/V)RT.
- Use the ideal gas law to calculate the number of moles of the gas, if the total pressure and volume are known.
- Apply the Dalton's law of partial pressures, which states that the total pressure of a mixture of gases is equal to the sum of the partial pressures of each gas.
For example, let's calculate the partial pressure of oxygen in a mixture of gases at a total pressure of 1 atm, temperature of 298 K, and volume of 10 L. Assuming the number of moles of oxygen is 0.2 mol, the partial pressure of oxygen can be calculated as: P(O2) = (0.2/10) x 0.08206 x 298 = 0.49 atm.
Applications of Partial Pressure
The concept of partial pressure has numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Respiratory physiology: to understand the transport of oxygen and carbon dioxide in the bloodstream.
- Chemical engineering: to design and optimize systems that involve the compression and expansion of gases.
- Environmental science: to study the behavior of greenhouse gases and their impact on the environment.
What is the significance of partial pressure in chemistry?
+The concept of partial pressure is crucial in chemistry as it helps to calculate the equilibrium constant of a reaction, predict the direction of a reaction, and determine the solubility of gases in liquids.
How do I calculate the partial pressure of a gas?
+To calculate the partial pressure of a gas, you need to know the number of moles of the gas, the volume of the container, the gas constant, and the temperature in Kelvin. You can use the formula: P = (n/V)RT.
In conclusion, calculating partial pressure is a straightforward process that requires knowledge of the number of moles of the gas, the volume of the container, the gas constant, and the temperature in Kelvin. Understanding the concept of partial pressure is essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and engineering. By applying the formulas and principles outlined in this article, you can easily calculate the partial pressure of a gas and gain a deeper understanding of the behavior of gases in various systems.



