Parallel Axis Theorem

The Parallel Axis Theorem, also known as the Huygens-Steiner theorem, is a fundamental concept in physics and engineering that describes the relationship between the moment of inertia of an object about a given axis and its moment of inertia about a parallel axis. This theorem is crucial in understanding the dynamics of rotating objects and has numerous applications in various fields, including mechanics, aerospace engineering, and robotics.
Introduction to the Parallel Axis Theorem
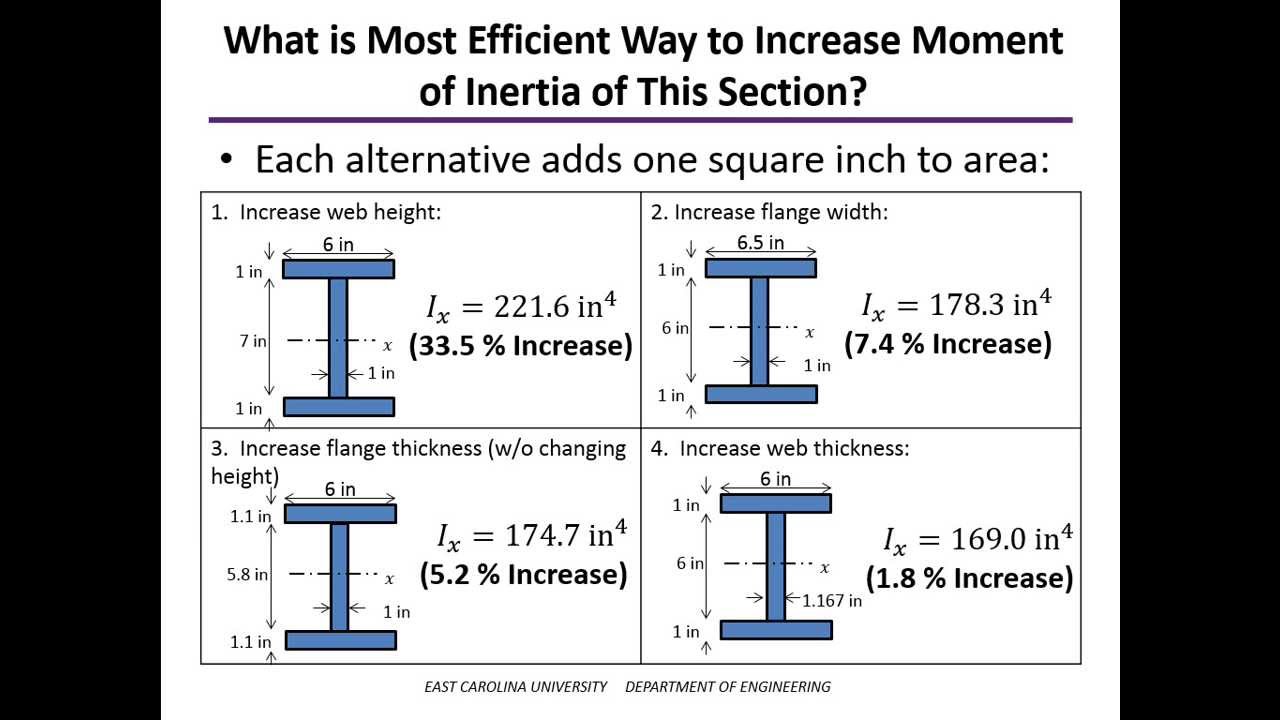
The moment of inertia is a measure of an object’s resistance to changes in its rotational motion. It depends on the mass distribution of the object and the axis of rotation. The Parallel Axis Theorem states that the moment of inertia of an object about a given axis is equal to the moment of inertia about a parallel axis, plus the product of the mass of the object and the square of the distance between the two axes. Mathematically, this can be expressed as I = I_cm + md^2, where I is the moment of inertia about the given axis, I_cm is the moment of inertia about the parallel axis passing through the center of mass, m is the mass of the object, and d is the distance between the two axes.
Derivation of the Parallel Axis Theorem
The derivation of the Parallel Axis Theorem involves considering the moment of inertia of an object about a given axis and then transforming it to a parallel axis. This can be done by using the moment of inertia tensor, which is a mathematical representation of the moment of inertia in three-dimensional space. By applying the tensor transformation rules, it can be shown that the moment of inertia about a parallel axis is given by the above equation. This derivation is based on the principles of classical mechanics and the definition of the moment of inertia as a measure of an object’s resistance to rotational motion.
| Moment of Inertia | Axis | Distance |
|---|---|---|
| I_cm | Parallel axis through center of mass | 0 |
| I | Given axis | d |

Applications of the Parallel Axis Theorem

The Parallel Axis Theorem has numerous applications in various fields, including aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, and robotics. For example, in the design of aircraft and spacecraft, the moment of inertia is critical in determining the stability and control of the vehicle. By applying the Parallel Axis Theorem, engineers can calculate the moment of inertia of the vehicle about its various axes, taking into account the distribution of mass and the location of the axes. Similarly, in robotics, the moment of inertia is important in determining the dynamics of robotic arms and other mechanisms, and the Parallel Axis Theorem provides a useful tool for calculating these moments of inertia.
Example Calculations
Consider a uniform rod of length L and mass M, rotating about an axis perpendicular to its length and passing through one of its ends. The moment of inertia of the rod about this axis can be calculated using the Parallel Axis Theorem. First, we calculate the moment of inertia about the axis passing through the center of mass of the rod, which is given by I_cm = (1⁄12)ML^2. Then, we apply the Parallel Axis Theorem to find the moment of inertia about the axis passing through one of the ends, which is given by I = I_cm + Md^2 = (1⁄12)ML^2 + M(L/2)^2 = (1⁄3)ML^2. This calculation demonstrates the application of the Parallel Axis Theorem in a simple yet practical example.
- Calculate the moment of inertia of a uniform disk about an axis perpendicular to its plane and passing through its center.
- Calculate the moment of inertia of a rectangular plate about an axis perpendicular to its plane and passing through one of its corners.
- Calculate the moment of inertia of a complex object, such as a robotic arm, about its various axes.
What is the significance of the Parallel Axis Theorem in physics and engineering?
+The Parallel Axis Theorem is significant because it provides a powerful tool for calculating the moment of inertia of complex objects, which is essential in understanding their rotational dynamics and stability. It has numerous applications in various fields, including aerospace engineering, mechanical engineering, and robotics.
How is the moment of inertia related to the mass distribution of an object?
+The moment of inertia is directly related to the mass distribution of an object. It depends on the distance of the mass elements from the axis of rotation and the mass of the object. The Parallel Axis Theorem provides a mathematical relationship between the moment of inertia and the mass distribution, allowing us to calculate the moment of inertia about different axes.