Official Language Of India

The official language of India is Hindi, as per the Constitution of India. However, it's essential to note that India is a multilingual country with a diverse population speaking various languages. The country has recognized 22 official languages, including Hindi, which is the primary official language used for central government administration. The other official languages are Assamese, Bengali, Bodo, Dogri, Gujarati, Kannada, Kashmiri, Konkani, Maithili, Malayalam, Manipuri, Marathi, Nepali, Odia, Punjabi, Sanskrit, Santhali, Sindhi, Tamil, Telugu, and Urdu.
History and Evolution of Official Language

The history of the official language of India dates back to the British colonial era. During this period, English was the primary language used for administrative purposes. After India gained independence in 1947, there was a need to establish a national language. Hindi was chosen as the official language due to its widespread use and geographical presence. The Official Languages Act of 1963 recognized Hindi as the primary official language, and it has been used in central government administration since then.
Importance of Hindi as Official Language
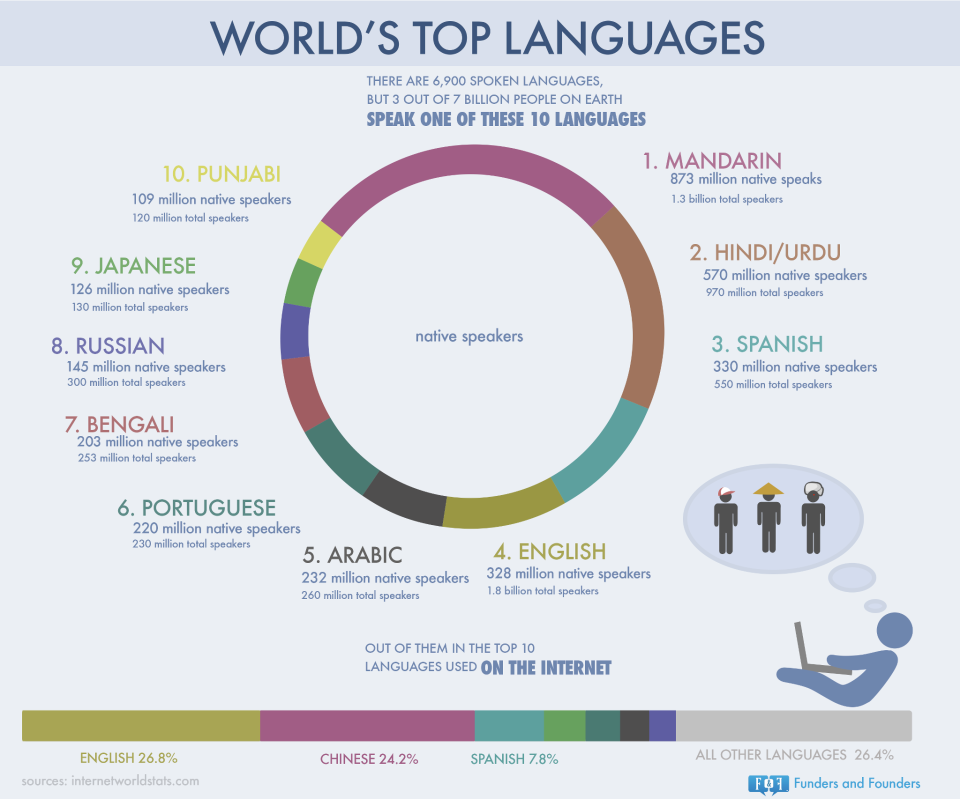
Hindi is the most widely spoken language in India, with over 500 million speakers. It is used as a lingua franca, allowing people from different regions to communicate with each other. The use of Hindi as the official language has facilitated national integration and unity. Hindi is used in government offices, courts, and educational institutions, making it an essential language for citizens to interact with the government and access public services. Additionally, Hindi is the primary language used in the media, including newspapers, television, and radio, which has contributed to its widespread popularity.
| Language | Number of Speakers |
|---|---|
| Hindi | 543 million |
| Bengali | 103 million |
| Marathi | 83 million |
| Telugu | 75 million |
| Tamil | 74 million |
Regional Languages and Their Significance
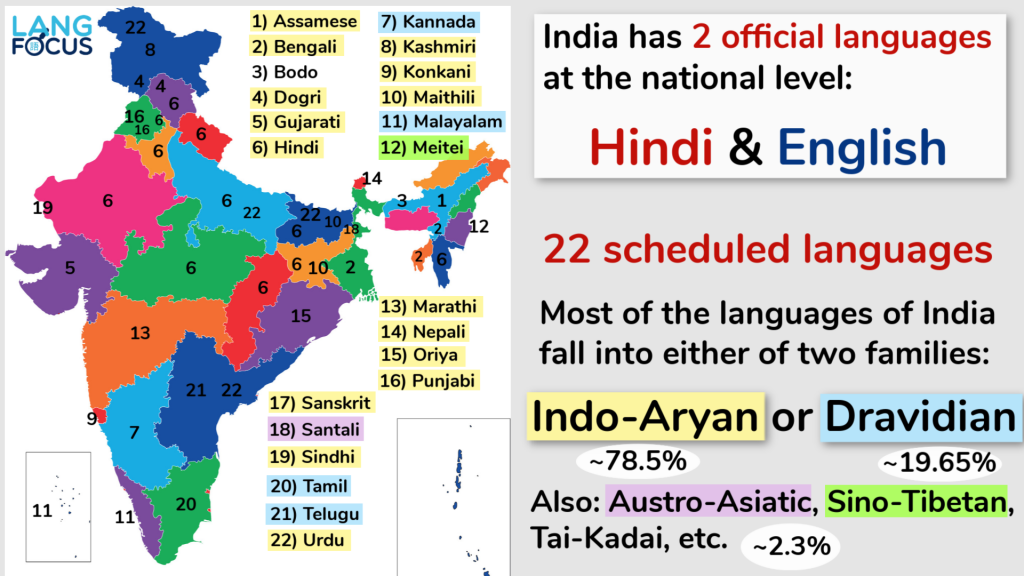
India’s regional languages play a vital role in the country’s linguistic diversity. Each state has its own official language, which is used in government administration, education, and media. The use of regional languages has helped to preserve cultural heritage and promote local identity. For example, Tamil is the official language of Tamil Nadu, and it is used in all aspects of government and public life. Similarly, Bengali is the official language of West Bengal, and it is an essential part of the state’s culture and identity.
Language Policy and Education
The Indian government has implemented a language policy that recognizes the importance of regional languages in education. The Three-Language Formula is a policy that requires students to study three languages: Hindi, English, and their mother tongue. This policy aims to promote linguistic diversity and ensure that students have access to education in their native languages. Additionally, the government has established institutions to promote the use of regional languages, such as the Central Institute of Indian Languages, which works to develop and promote the use of Indian languages.
- The Three-Language Formula is implemented in all states and union territories.
- The formula requires students to study Hindi, English, and their mother tongue.
- The policy aims to promote linguistic diversity and ensure that students have access to education in their native languages.
What is the official language of India?
+The official language of India is Hindi, as per the Constitution of India. However, India is a multilingual country with a diverse population speaking various languages, and there are 22 recognized official languages.
Why was Hindi chosen as the official language?
+Hindi was chosen as the official language due to its widespread use and geographical presence. It is the most widely spoken language in India, with over 500 million speakers.
What is the significance of regional languages in India?
+Regional languages play a vital role in India’s linguistic diversity. Each state has its own official language, which is used in government administration, education, and media. The use of regional languages has helped to preserve cultural heritage and promote local identity.