Molar Mass Of Hydrogen Peroxide

The molar mass of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) is a fundamental concept in chemistry, crucial for understanding its properties, behavior, and reactions. Hydrogen peroxide is a compound made up of two hydrogen atoms and two oxygen atoms. To calculate its molar mass, we need to know the atomic masses of hydrogen and oxygen. The atomic mass of hydrogen (H) is approximately 1.00794 g/mol, and the atomic mass of oxygen (O) is approximately 15.9994 g/mol.
Calculation of Molar Mass

To find the molar mass of hydrogen peroxide, we sum the atomic masses of its constituent atoms. The formula for hydrogen peroxide is H2O2, indicating it has 2 hydrogen atoms and 2 oxygen atoms. Thus, the molar mass of H2O2 can be calculated as follows: (2 * atomic mass of H) + (2 * atomic mass of O). Substituting the atomic masses: (2 * 1.00794 g/mol) + (2 * 15.9994 g/mol).
Performing the calculation: (2 * 1.00794 g/mol) = 2.01588 g/mol for the hydrogen atoms, and (2 * 15.9994 g/mol) = 31.9988 g/mol for the oxygen atoms. Adding these together gives a molar mass of 2.01588 g/mol + 31.9988 g/mol = 34.01468 g/mol. Rounding to a more conventional precision, the molar mass of hydrogen peroxide is approximately 34.01 g/mol.
Importance of Molar Mass in Chemistry
The molar mass of a compound like hydrogen peroxide is critical in various chemical calculations, such as determining the number of moles of a substance, calculating the mass of a substance needed for a reaction, and understanding the stoichiometry of chemical reactions. In the context of hydrogen peroxide, knowing its molar mass is essential for applications ranging from bleaching and disinfection to its use as a propellant in rocketry.
In chemical reactions involving hydrogen peroxide, such as its decomposition into water and oxygen (2H2O2 → 2H2O + O2), the molar mass is used to calculate the amounts of reactants and products. This is crucial for ensuring the reaction is carried out safely and efficiently, with the correct proportions of substances to achieve the desired outcome.
| Element | Atomic Mass (g/mol) | Number of Atoms in H2O2 | Contribution to Molar Mass (g/mol) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hydrogen (H) | 1.00794 | 2 | 2.01588 |
| Oxygen (O) | 15.9994 | 2 | 31.9988 |
| Total Molar Mass of H2O2 | 34.01468 |
Applications and Considerations
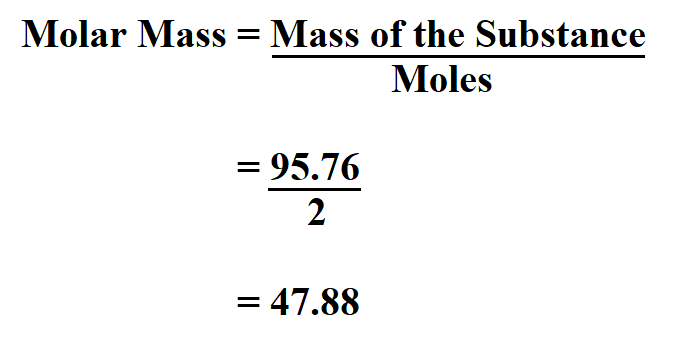
Hydrogen peroxide’s applications are diverse, ranging from household use as a disinfectant to industrial applications in paper bleaching, textile manufacturing, and as a component in fuel cells. In each of these applications, the molar mass of hydrogen peroxide plays a critical role in determining the concentration of solutions, the amount of substance required for specific reactions, and the efficiency of processes.
For example, in the production of propylene oxide, hydrogen peroxide is used as a green alternative to traditional methods, offering a more environmentally friendly route to this important chemical intermediate. The molar mass of hydrogen peroxide is essential in calculating the stoichiometric ratios required for this reaction, ensuring optimal conditions for the production process.
Future Implications and Research
As research continues into more efficient and sustainable uses of hydrogen peroxide, its molar mass will remain a cornerstone of scientific investigation. Advances in catalysis and materials science are expected to further expand the applications of hydrogen peroxide, from energy storage and generation to advanced water treatment technologies. Understanding the fundamental properties of hydrogen peroxide, including its molar mass, will be crucial in unlocking these future applications.
The development of more efficient catalysts for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide into oxygen and water could have significant implications for space exploration, where hydrogen peroxide is used as a monopropellant for thrusters. More efficient use of hydrogen peroxide could lead to longer mission durations and reduced logistical challenges for space agencies and private space companies.
What is the significance of the molar mass of hydrogen peroxide in chemical reactions?
+The molar mass of hydrogen peroxide is significant because it allows for the calculation of the number of moles of the substance, which is essential for understanding reaction stoichiometry, preparing solutions of specific concentrations, and predicting the quantities of reactants and products in chemical reactions.
How does the molar mass of hydrogen peroxide impact its industrial applications?
+The molar mass of hydrogen peroxide is crucial for its industrial applications, as it influences the calculation of the amounts of substance needed for specific processes, the efficiency of reactions, and the cost-effectiveness of using hydrogen peroxide as a reactant or reagent. This is particularly important in large-scale productions where small discrepancies in chemical quantities can significantly affect product quality and process economics.



