Is Couscous Pasta
Couscous is often mistaken for a type of pasta due to its appearance and the way it is consumed in various dishes. However, it is actually a traditional North African dish made from crushed durum wheat semolina. The semolina is moistened and then rolled into small balls, which are subsequently dried. This process gives couscous its unique texture, which is often compared to pasta but is technically a type of paste or dough that has been worked and dried.
Origins and History of Couscous

Couscous has its roots in the Maghreb region of North Africa, which includes countries such as Morocco, Algeria, and Tunisia. The dish is believed to have originated among the Berbers, who are the indigenous people of the region. Over time, couscous spread throughout the Mediterranean and has become a staple in many Middle Eastern and African cuisines. Despite its widespread adoption, couscous remains a deeply cultural and symbolic food in North African societies, often served at special occasions and holidays.
Preparation and Consumption
Couscous is typically prepared by steaming the dried semolina balls over boiling water, often flavored with spices and herbs. This process allows the couscous to absorb the flavors and aromas of the surrounding ingredients. Once cooked, couscous can be served with a variety of dishes, including stews, meats, and vegetables. In North African cuisine, it is common to serve couscous with a rich meat stew, known as tagine, which is slow-cooked in a clay pot with a conical lid.
| Type of Couscous | Description |
|---|---|
| Traditional Couscous | Hand-rolled semolina balls, often larger in size |
| Instant Couscous | Pre-steamed and dried, allowing for quicker preparation |
| Whole Wheat Couscous | Made from whole wheat semolina, offering a nuttier flavor and higher nutritional value |

Nutritional Value and Health Benefits

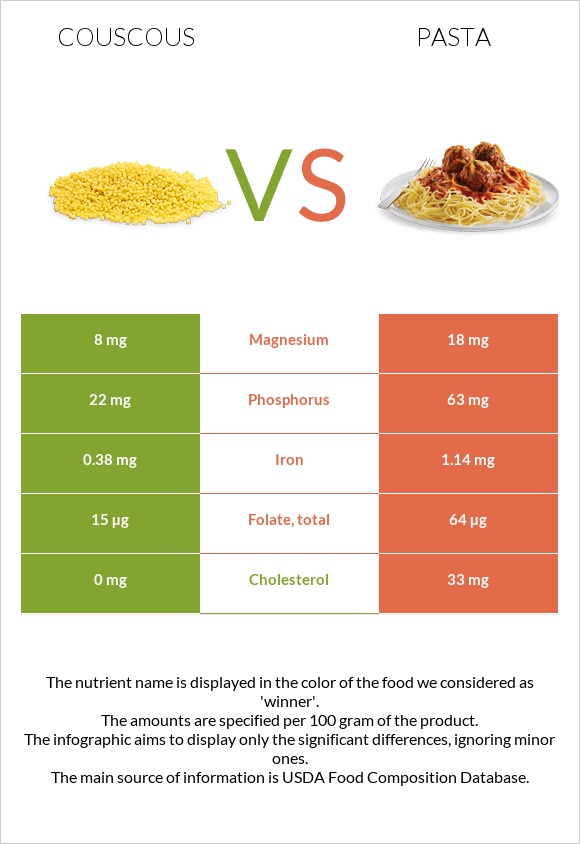
Couscous is a good source of carbohydrates, fiber, and several important minerals, including iron, magnesium, and selenium. It is also relatively low in calories and fat, making it a popular choice for health-conscious individuals. Whole wheat couscous, in particular, offers a higher nutritional value due to its higher content of fiber, vitamins, and minerals. Regular consumption of couscous has been linked to several health benefits, including improved digestion, reduced risk of heart disease, and enhanced immune function.
Cultural Significance and Variations
Couscous is a deeply cultural food that varies greatly from one region to another. In Morocco, for example, couscous is often served with a sweet and spicy sauce, while in Algeria, it is typically served with a rich meat stew. The dish is also an important part of many traditional holidays and celebrations, including weddings and festivals. The cultural significance of couscous is reflected in its preparation and consumption, which often involves a communal effort and a sense of shared identity.
What is the difference between couscous and pasta?
+Couscous is made from crushed durum wheat semolina, while pasta is typically made from wheat flour and water. The two dishes also differ in terms of preparation and texture, with couscous being steamed and having a lighter, fluffier texture.
Is couscous a healthy food option?
+Yes, couscous is a relatively healthy food option, low in calories and fat and high in fiber and several important minerals. Whole wheat couscous, in particular, offers a higher nutritional value due to its higher content of fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
In conclusion, couscous is a unique and culturally significant food that offers a range of health benefits and culinary possibilities. While it may be mistaken for a type of pasta, its preparation, texture, and nutritional value set it apart as a distinct and valuable part of many traditional cuisines. Whether served as a side dish or used as a base for a variety of flavors and ingredients, couscous is a versatile and delicious food that is sure to continue to play an important role in many cultures around the world.
Related Terms:
- is couscous easy to digest
- what does couscous taste like