Conduction Made Easy: Key Concepts
Conduction, a fundamental concept in physics and engineering, refers to the transfer of heat or energy through a medium, such as a solid, liquid, or gas, without the physical movement of the medium itself. Understanding conduction is crucial for designing efficient heating and cooling systems, as well as for optimizing the performance of various technological devices. In this article, we will delve into the key concepts of conduction, exploring the underlying principles, mechanisms, and applications of this essential phenomenon.
Introduction to Conduction

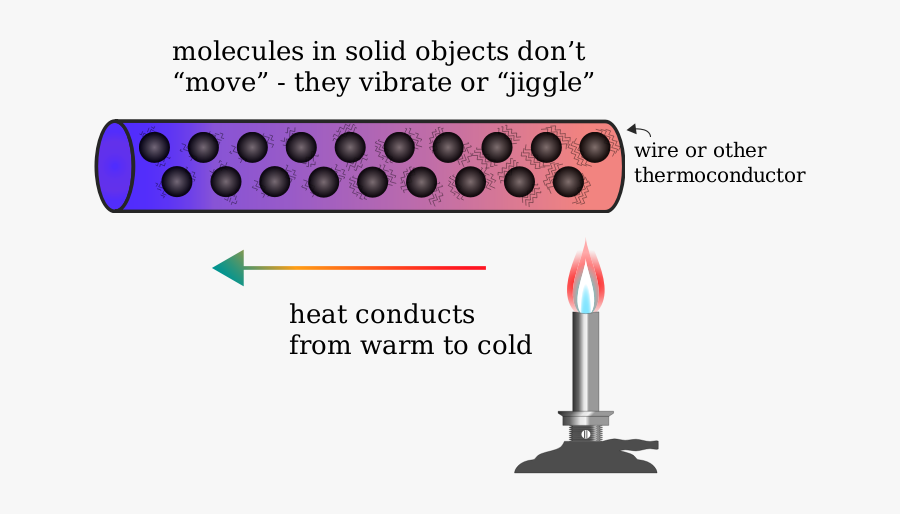
Conduction occurs when there is a temperature difference between two objects or within a single object. The flow of heat energy from an area of higher temperature to an area of lower temperature is driven by the kinetic energy of particles, such as atoms, molecules, or electrons. In solids, conduction is facilitated by the vibration of atoms and the movement of free electrons. In liquids and gases, conduction is primarily due to the collisions and interactions between particles. The rate of heat transfer through conduction is influenced by factors such as the temperature difference, the properties of the material, and the geometry of the system.
Key Factors Influencing Conduction
Several key factors affect the efficiency of conduction, including thermal conductivity, specific heat capacity, and density. Thermal conductivity, typically denoted by the symbol λ (lambda), is a measure of a material’s ability to conduct heat. Materials with high thermal conductivity, such as copper and silver, are excellent heat conductors, while materials with low thermal conductivity, such as air and vacuum, are poor conductors. Specific heat capacity, which represents the amount of heat energy required to change the temperature of a unit mass of a substance by one degree, also plays a crucial role in determining the conduction rate. Additionally, the density of a material can impact its thermal conductivity, as denser materials tend to have higher thermal conductivity values.
| Material | Thermal Conductivity (W/m·K) |
|---|---|
| Copper | 386 |
| Silver | 429 |
| Aluminum | 237 |
| Air | 0.024 |
| Vacuum | 0 |

Mechanisms of Conduction

Conduction can occur through various mechanisms, including electron diffusion, phonon transport, and radiative transfer. In metals, electron diffusion is the primary mechanism of conduction, where free electrons carry heat energy through the material. In non-metals, phonon transport, which involves the vibration of atoms, is the dominant mechanism. Radiative transfer, which occurs through the emission and absorption of photons, can also contribute to conduction, particularly in high-temperature applications.
Applications of Conduction
Conduction has numerous practical applications in various fields, including heat transfer, electronics, and energy systems. In heat transfer, conduction is used in heat exchangers, such as radiators and condensers, to efficiently transfer heat energy between fluids. In electronics, conduction is critical for the design of thermal management systems, which aim to dissipate heat generated by electronic components. In energy systems, conduction is used in solar panels and thermoelectric devices to convert heat energy into electrical energy.
- Heat exchangers
- Thermal management systems
- Solar panels
- Thermoelectric devices
- Cryogenic systems
What is the difference between conduction and convection?
+Conduction refers to the transfer of heat energy through a medium without the physical movement of the medium, while convection involves the transfer of heat energy through the movement of fluids.
How does the thermal conductivity of a material affect its conduction rate?
+The thermal conductivity of a material determines its ability to conduct heat. Materials with high thermal conductivity values, such as copper and silver, are more efficient at conducting heat than materials with low thermal conductivity values, such as air and vacuum.
In conclusion, conduction is a vital phenomenon that plays a crucial role in various technological applications. Understanding the key concepts, mechanisms, and applications of conduction is essential for designing efficient heat transfer systems, optimizing electronic devices, and developing innovative energy solutions. By recognizing the importance of conduction and its underlying principles, researchers and engineers can continue to push the boundaries of technological advancements, enabling the creation of more efficient, sustainable, and powerful systems.


