10 Oxygen Atomic Mass Facts To Know

The atomic mass of oxygen is a fundamental concept in chemistry, and understanding its properties and behavior is crucial for various scientific and industrial applications. Oxygen, denoted by the symbol O, is the third most abundant element in the universe by mass and plays a vital role in supporting life on Earth. In this article, we will delve into the top 10 oxygen atomic mass facts that are essential to know.
Introduction to Oxygen Atomic Mass

Oxygen’s atomic mass is approximately 15.9994 u (unified atomic mass units), which is a weighted average of the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes. The most abundant isotope of oxygen is oxygen-16, which accounts for about 99.76% of the element’s natural abundance. The atomic mass of oxygen is a critical parameter in various chemical reactions, including combustion, respiration, and photosynthesis.
Isotopes of Oxygen
Oxygen has three naturally occurring isotopes: oxygen-16, oxygen-17, and oxygen-18. These isotopes have different numbers of neutrons in their atomic nuclei, which affect their masses. The masses of these isotopes are 15.994915 u, 16.999132 u, and 17.999161 u, respectively. Understanding the properties and abundance of these isotopes is essential for various scientific applications, including geology, biology, and environmental science.
| Isotope | Mass (u) | Natural Abundance (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen-16 | 15.994915 | 99.76 |
| Oxygen-17 | 16.999132 | 0.0379 |
| Oxygen-18 | 17.999161 | 0.2049 |
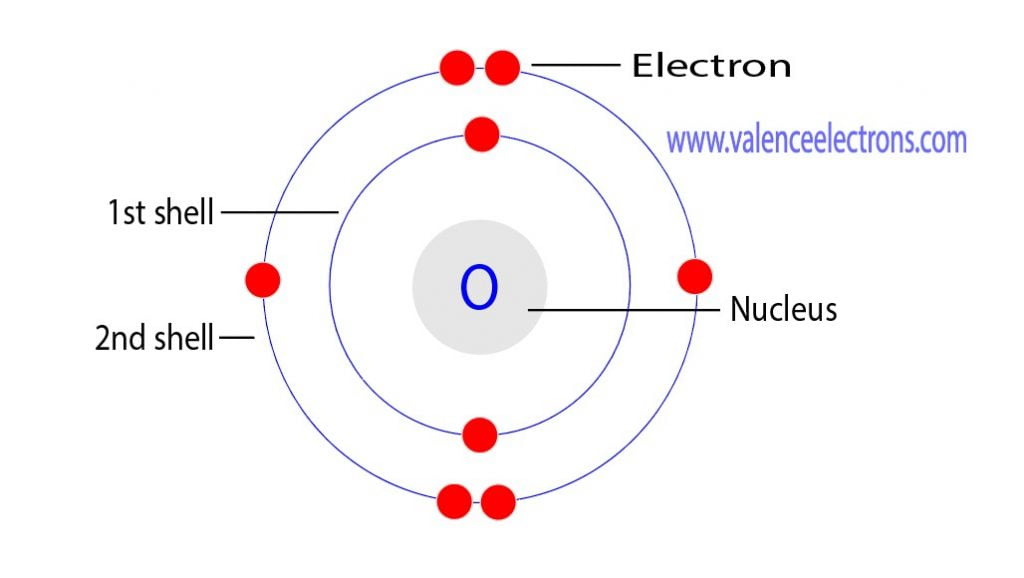
Chemical Properties of Oxygen

Oxygen is a highly reactive element that readily forms compounds with other elements. Its atomic mass and electron configuration play a crucial role in determining its chemical properties. Oxygen is a strong oxidizing agent and is essential for various chemical reactions, including combustion, corrosion, and respiration. Understanding the chemical properties of oxygen is vital for various industrial and scientific applications.
Physical Properties of Oxygen
Oxygen is a colorless, odorless, and tasteless gas at room temperature and pressure. Its physical properties, such as melting point, boiling point, and density, are essential for various scientific and industrial applications. The melting point of oxygen is -218.79 °C, and its boiling point is -182.962 °C. The density of oxygen is approximately 1.141 g/L, which is essential for calculating its mass and volume in various applications.
The atomic mass of oxygen is a critical parameter in determining its physical and chemical properties. The electron configuration of oxygen is 1s² 2s² 2p⁴, which plays a vital role in determining its reactivity and chemical behavior. Understanding the physical and chemical properties of oxygen is essential for various scientific and industrial applications.
Industrial Applications of Oxygen
Oxygen is a critical element in various industrial applications, including steel production, water treatment, and medical therapy. Its atomic mass and chemical properties make it an essential component in various chemical reactions and processes. The production of steel, for example, requires large quantities of oxygen to remove impurities and achieve the desired chemical composition.
The industrial production of oxygen involves the distillation of liquid air, which is a complex process that requires careful control of temperature and pressure. The cost of production is a critical factor in determining the economic viability of oxygen production, which is essential for various industrial applications. Understanding the industrial applications of oxygen is vital for optimizing production processes and reducing costs.
What is the atomic mass of oxygen?
+The atomic mass of oxygen is approximately 15.9994 u (unified atomic mass units), which is a weighted average of the masses of its naturally occurring isotopes.
What are the naturally occurring isotopes of oxygen?
+Oxygen has three naturally occurring isotopes: oxygen-16, oxygen-17, and oxygen-18, which have different numbers of neutrons in their atomic nuclei.
In conclusion, the atomic mass of oxygen is a critical parameter that plays a vital role in determining its physical and chemical properties. Understanding the properties and behavior of oxygen is essential for various scientific and industrial applications. By recognizing the importance of oxygen’s atomic mass and its isotopes, we can optimize production processes, reduce costs, and advance our knowledge of the natural world.



